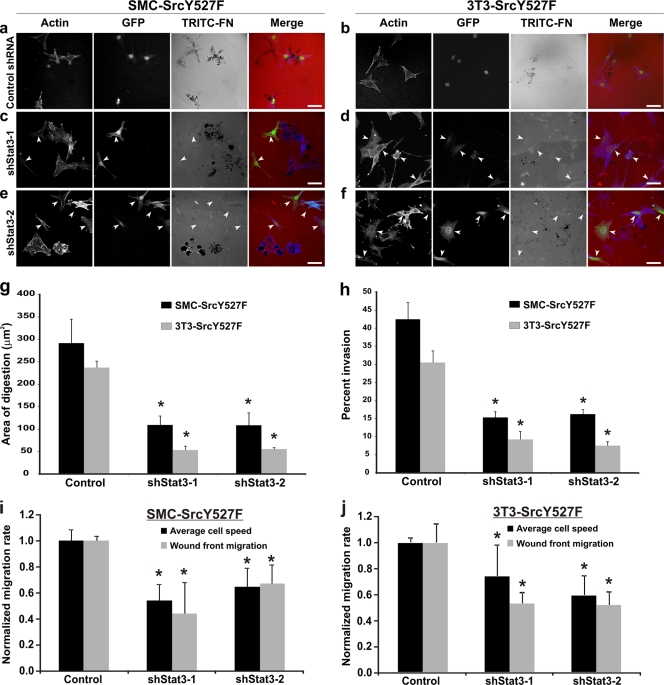
FIG. 2.
Stat3 knockdown adversely affects ECM degradation, Matrigel invasion, and cell migration induced by SrcY527F in SMC and 3T3 cells. (a to f) SrcY527F cells stably transduced with either a control shRNA-GFP (a and b) or a Stat3-targeted shRNA-GFP (c to f) were used to study the effect of Stat3 knockdown on Src-induced ECM digestion. Cells were cultured on gelatin-coated coverslips layered with TRITC-fibronectin (TRITC-FN) for 7 h. Cells expressing shStat3 (marked with arrowheads) were monitored by GFP expression. Actin was labeled with phalloidin 350. Bars, 20 μm. (g) Quantitative measurements were performed to determine the area of ECM digestion for each cell type. Thirty cells for each category were measured for the area of digestion (in μm2) in the migration path of the cell after 7 h. (h) SMC- or 3T3-derived cell lines expressing the indicated constructs were examined in order to determine their ability to invade Matrigel. The number of cells that migrated through the screen was counted, and the percentage of invasion was determined by dividing the invasion number (Matrigel-coated screen) by the migrating number (uncoated screen). (i and j) A scratch-induced wound-healing assay was performed to determine the average migration rate of individual cells as well as the speed of wound front migration (wound closure) in SMC-SrcY527F (i) and 3T3-SrcY527F (j) cells expressing either an empty vector (control) or a shRNA against Stat3 (shStat3-1 or shStat3-2). Error bars represent standard deviations for three separate experiments. P values were determined using a two-sided, equal-variance Student t test. *, significant difference (P < 0.05) from the value for the respective control.