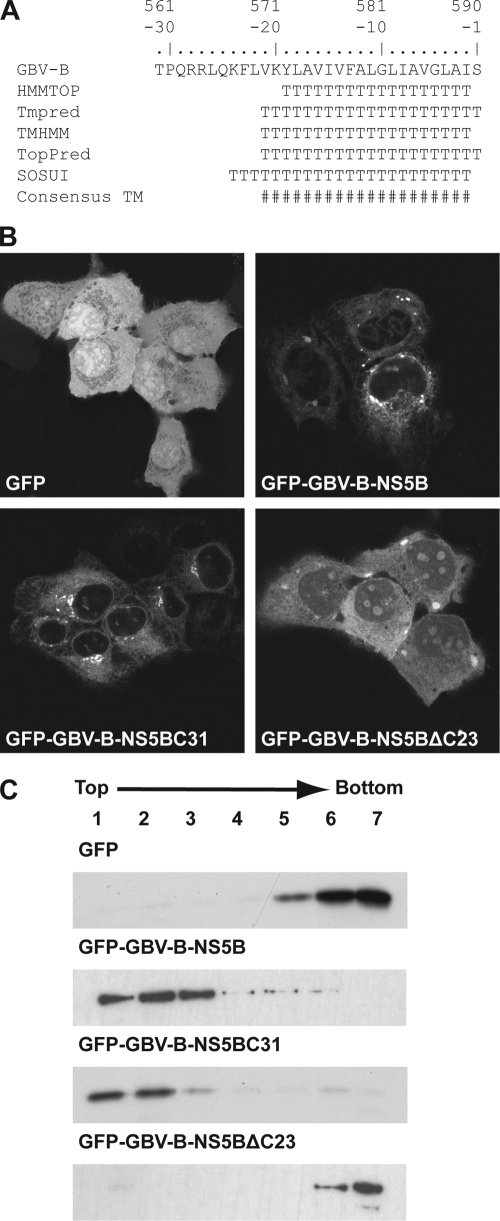
FIG. 1.
The C-terminal 23 amino acids of GBV-B NS5B mediate membrane association. (A) Sequence analyses of the GBV-B NS5B C terminus. Amino acids are numbered with respect to the NS5B protein and negatively from its C terminus. The following methods to predict TMDs were combined: HMMTOP (http://www.enzim.hu/hmmtop/), Tmpred (http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/TMPRED_form.html), TMHMM (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM), TopPred (http://mobyle.pasteur.fr/cgi-bin/MobylePortal/portal.py?form_toppred), and SOSUI (http://bp.nuap.nagoya-u.ac.jp/sosui/). T, predicted transmembrane amino acid; #, consensus minimum transmembrane segment, considering all prediction methods. (B) Subcellular localization of GFP fusion constructs. Plasmids pCMVGFP, pCMVGFP-GBV-B-NS5B, pCMVGFP-GBV-B-NS5BC31, and pCMVGFP-GBV-B-NS5BΔC23 were transfected into U2-OS cells, followed by fixation and confocal laser scanning microscopy. (C) Membrane flotation analyses. Hypotonic lysates of U-2 OS cells transfected with the constructs above were analyzed by equilibrium centrifugation through 5 to 37.5% (wt/vol) Nycodenz gradients. Fractions were collected from the top and analyzed by immunoblotting using monoclonal antibody JL-8 against GFP (Clontech, Palo Alto, CA). Under these conditions, membranes and associated proteins float to the upper, low-density fractions while soluble and aggregated material remains in the lower, high-density fractions.