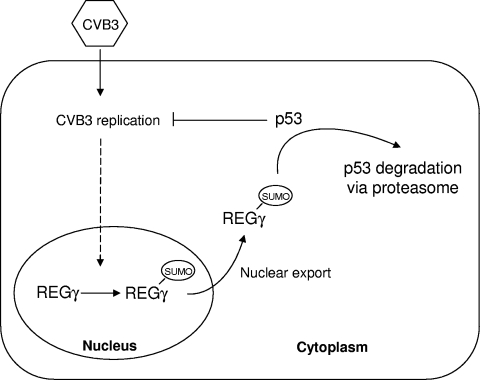
FIG. 9.
Proposed mechanism by which REGγ enhances CVB3 infectivity. Following CVB3 infection, REGγ is sumoylated and exported from the nucleus. Cytoplasmic translocation of REGγ facilitates proteasomal degradation of tumor suppressor protein p53, which subsequently enhances CVB3 infection by suppressing the inhibitory effect of p53 on viral replication.