Abstract
Recent advances in molecular genetics have revealed the mechanisms underlying a variety of inherited human disorders. Among them, mutations in G protein-coupled receptors have clearly demonstrated two types of abnormalities, namely loss of function and constitutive activation of the receptors. Thromboxane A2 (TXA2) receptor is a member of the family of G protein-coupled receptors and performs an essential role in hemostasis by interacting with TXA2 to induce platelet aggregation. Here we identify a single amino acid substitution (Arg60-->Leu) in the first cytoplasmic loop of the TXA2 receptor in a dominantly inherited bleeding disorder characterized by defective platelet response to TXA2. This mutation was found exclusively in affected members of two unrelated families with the disorder. The mutant receptor expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells showed decreased agonist-induced second messenger formation despite its normal ligand binding affinities. These results suggest that the Arg60 to Leu mutation is responsible for the disorder. Moreover, dominant inheritance of the disorder suggests the possibility that the mutation produces a dominant negative TXA2 receptor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong R. A., Jones R. L., Peesapati V., Will S. G., Wilson N. H. Competitive antagonism at thromboxane receptors in human platelets. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Mar;84(3):595–607. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb16139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORN G. V. Aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate and its reversal. Nature. 1962 Jun 9;194:927–929. doi: 10.1038/194927b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Young A. C., Brann M. R., Buckley N. J. Cloning and expression of the human and rat m5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor genes. Neuron. 1988 Jul;1(5):403–410. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Shaller C. C., Belmonte E. J. Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate-induced granule secretion in platelets. Evidence that the activation of phospholipase C mediated by platelet thromboxane receptors involves a guanine nucleotide binding protein-dependent mechanism distinct from that of thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1269–1275. doi: 10.1172/JCI112947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham D. E. Mutations in G protein-linked receptors: novel insights on disease. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1237–1239. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90609-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong T. M., Anderson S. A., Yu H., Huang R. R., Strader C. D. Differential activation of intracellular effector by two isoforms of human neurokinin-1 receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;41(1):24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frielle T., Collins S., Daniel K. W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Kobilka B. K. Cloning of the cDNA for the human beta 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7920–7924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuse I., Mito M., Hattori A., Higuchi W., Shibata A., Ushikubi F., Okuma M., Yahata K. Defective signal transduction induced by thromboxane A2 in a patient with a mild bleeding disorder: impaired phospholipase C activation despite normal phospholipase A2 activation. Blood. 1993 Feb 15;81(4):994–1000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardisty R. M., Machin S. J., Nokes T. J., Rink T. J., Smith S. W. A new congenital defect of platelet secretion: impaired responsiveness of the platelets to cytoplasmic free calcium. Br J Haematol. 1983 Apr;53(4):543–557. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb07306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori A., Takahashi H., Takahashi M., Shibata A., Okuma M. A new familial defect of platelet release mechanism (the intracellular Ca++ transport defect?). Nihon Ketsueki Gakkai Zasshi. 1981 Jul;44(4):969–972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
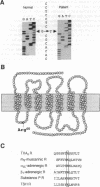
- Hirata M., Hayashi Y., Ushikubi F., Yokota Y., Kageyama R., Nakanishi S., Narumiya S. Cloning and expression of cDNA for a human thromboxane A2 receptor. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):617–620. doi: 10.1038/349617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Bojanic D., Wilson A. Platelet activating factor and U44069 stimulate a GTPase activity in human platelets which is distinct from the guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins, Ns and Ni. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 15;234(3):737–740. doi: 10.1042/bj2340737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakizuka A., Miller W. H., Jr, Umesono K., Warrell R. P., Jr, Frankel S. R., Murty V. V., Dmitrovsky E., Evans R. M. Chromosomal translocation t(15;17) in human acute promyelocytic leukemia fuses RAR alpha with a novel putative transcription factor, PML. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):663–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90112-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lages B., Malmsten C., Weiss H. J., Samuelsson B. Impaired platelet response to thromboxane-A2 and defective calcium mobilization in a patient with a bleeding disorder. Blood. 1981 Mar;57(3):545–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J. G-protein-coupled receptors. Turned on to ill effect. Nature. 1993 Oct 14;365(6447):603–604. doi: 10.1038/365603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomasney J. W., Lorenz W., Allen L. F., King K., Regan J. W., Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Expansion of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor family: cloning and characterization of a human alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype, the gene for which is located on chromosome 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5094–5098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machin S. J., Keenan J. P., McVerry B. A. Defective platelet aggregation to the calcium ionophore A23187 in a patient with a lifelong bleeding disorder. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Oct;36(10):1140–1144. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.10.1140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggio R., Vogel Z., Wess J. Coexpression studies with mutant muscarinic/adrenergic receptors provide evidence for intermolecular "cross-talk" between G-protein-linked receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):3103–3107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.3103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min K. C., Zvyaga T. A., Cypess A. M., Sakmar T. P. Characterization of mutant rhodopsins responsible for autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Mutations on the cytoplasmic surface affect transducin activation. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9400–9404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misrahi M., Loosfelt H., Atger M., Sar S., Guiochon-Mantel A., Milgrom E. Cloning, sequencing and expression of human TSH receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 15;166(1):394–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91958-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S., Nagata S. pEF-BOS, a powerful mammalian expression vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5322–5322. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
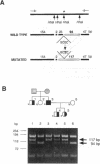
- Nüsing R. M., Hirata M., Kakizuka A., Eki T., Ozawa K., Narumiya S. Characterization and chromosomal mapping of the human thromboxane A2 receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):25253–25259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Hnatowich M., Regan J. W., Leader W. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Site-directed mutagenesis of the cytoplasmic domains of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Localization of regions involved in G protein-receptor coupling. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15985–15992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuma M., Takayama H., Uchino H. Subnormal platelet response to thromboxane A2 in a patient with chronic myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 1982 Jul;51(3):469–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb02804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter L. T., Ballesteros L. A., Bichajian L. H., Ferrendelli C. A., Fisher A., Hanchett H. E., Zhang R. Evidence of paired M2 muscarinic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;39(2):211–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter L. T., Ferrendelli C. A., Hanchett H. E. Two affinity states of M1 muscarine receptors. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1988 Jun;8(2):181–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00711244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. R., Cohen G. B., Zhukovsky E. A., Oprian D. D. Constitutively active mutants of rhodopsin. Neuron. 1992 Oct;9(4):719–725. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90034-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal W., Antaramian A., Gilbert S., Birnbaumer M. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. A V2 vasopressin receptor unable to stimulate adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13030–13033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal W., Seibold A., Antaramian A., Lonergan M., Arthus M. F., Hendy G. N., Birnbaumer M., Bichet D. G. Molecular identification of the gene responsible for congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nature. 1992 Sep 17;359(6392):233–235. doi: 10.1038/359233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samama M., Lecrubier C., Conard J., Hotchen M., Breton-Gorius J., Vargaftig B., Chignard M., Lagarde M., Dechavanne M. Constitutional thrombocytopathy with subnormal response to thromboxane A2. Br J Haematol. 1981 Jun;48(2):293–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenker A., Goldsmith P., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M. The G protein coupled to the thromboxane A2 receptor in human platelets is a member of the novel Gq family. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9309–9313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenker A., Laue L., Kosugi S., Merendino J. J., Jr, Minegishi T., Cutler G. B., Jr A constitutively activating mutation of the luteinizing hormone receptor in familial male precocious puberty. Nature. 1993 Oct 14;365(6447):652–654. doi: 10.1038/365652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel A. M., Weinstein L. S., Shenker A. Abnormalities in G protein-coupled signal transduction pathways in human disease. J Clin Invest. 1993 Sep;92(3):1119–1125. doi: 10.1172/JCI116680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushikubi F., Ishibashi T., Narumiya S., Okuma M. Analysis of the defective signal transduction mechanism through the platelet thromboxane A2 receptor in a patient with polycythemia vera. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Jan 23;67(1):144–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushikubi F., Nakajima M., Hirata M., Okuma M., Fujiwara M., Narumiya S. Purification of the thromboxane A2/prostaglandin H2 receptor from human blood platelets. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16496–16501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushikubi F., Okuma M., Kanaji K., Sugiyama T., Ogorochi T., Narumiya S., Uchino H. Hemorrhagic thrombocytopathy with platelet thromboxane A2 receptor abnormality: defective signal transduction with normal binding activity. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Apr 7;57(2):158–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenplas S., Wiid I., Grobler-Rabie A., Brebner K., Ricketts M., Wållis G., Bester A., Boyd C., Måthew C. Blot hybridisation analysis of genomic DNA. J Med Genet. 1984 Jun;21(3):164–172. doi: 10.1136/jmg.21.3.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu K. K., Le Breton G. C., Tai H. H., Chen Y. C. Abnormal platelet response to thromboxane A2. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;67(6):1801–1804. doi: 10.1172/JCI110221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu K. K., Minkoff I. M., Rossi E. C., Chen Y. C. Hereditary bleeding disorder due to a primary defect in platelet release reaction. Br J Haematol. 1981 Feb;47(2):241–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1981.tb02785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota Y., Sasai Y., Tanaka K., Fujiwara T., Tsuchida K., Shigemoto R., Kakizuka A., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA for rat substance P receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17649–17652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]