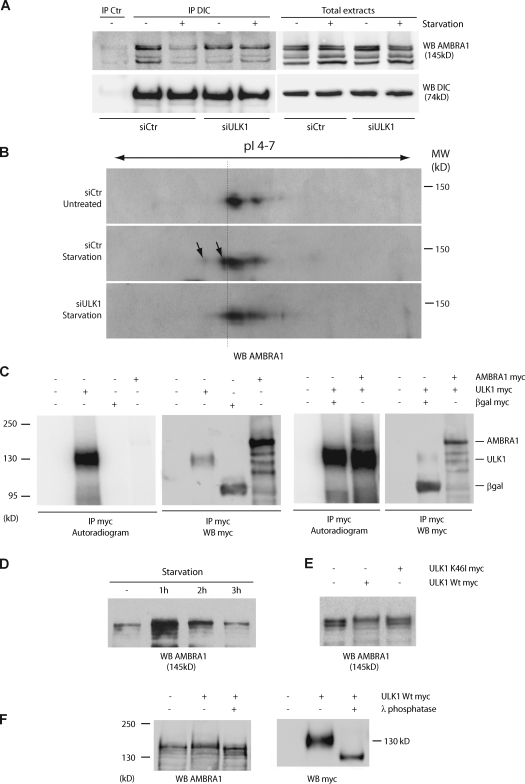
Figure 3.
AMBRA1 is phosphorylated during autophagy in an ULK1-dependent manner. (A) Down-regulation of ULK1 expression prevents AMBRA1 dissociation from the dynein motor complex during autophagy. ULK1 was down-regulated in 2F cells using specific siRNA oligonucleotides (siULK1). ULK1 expression level was analyzed by quantitative PCR and WB analyses (Fig. S2 A). siCtr, unrelated oligonucleotides. 48 h after transfection, 2F cells were starved for 4 h or left untreated. Protein extracts were prepared and subjected to IP using an anti-DIC (IP DIC) or an unrelated antibody (IP control [Ctr]) as a negative control. The purified complexes were analyzed by WB together with the corresponding total extracts using anti-DIC (WB DIC; bottom) and anti-AMBRA1 antibodies (WB AMBRA1; top). (B) Analysis of AMBRA1 modification after autophagy induction in control and ULK1 down-regulated cells. Protein extracts from samples as described in A were resolved by bidimensional gel electrophoresis (2DE) and analyzed by WB using an anti-AMBRA1 antibody. pI 4–7, isoelectric pH gradient 4–7; MW, molecular weight. AMBRA1 protein spots induced by starvation are indicated (arrows). Broken line highlights the isoelectric shift of the AMBRA1 isoforms produced by ULK1 activity. (C) Immunopurified ULK1 phosphorylates AMBRA1 in vitro. HEK293 cells were transfected with expression vectors encoding either AMBRA1 or ULK1 Myc-tagged proteins. 24 h after transfection, ULK1-expressing cells were nutrient starved for 2 h to stimulate ULK1 activity. Protein extracts were prepared from transfected cells and subject to IP using an anti-Myc antibody (IP Myc). An aliquot of the immunoprecipitated proteins was analyzed by WB using an anti-Myc antibody (WB Myc) to check for protein purification (right). Immunopurified ULK1 proteins were subjected to an in vitro kinase assay in the presence (+) or absence (−) of immunopurified AMBRA1 as described in Materials and methods. As negative control for kinase activity (−), the in vitro kinase assay was performed using anti-Myc–immunopurified complexes from βgal-transfected cells (βgal Myc). The reactions were resolved on SDS-PAGE and 32P-labeled proteins revealed by autoradiography (left). (D) Electrophoretic mobility hypershift of AMBRA1 upon autophagy induction. HEK293 cells were nutrient-starved for 1, 2, and 3 h. Protein extracts were prepared, loaded on a polyacrylamide gel (see Materials and methods) and analyzed by WB using an anti-AMBRA1 antibody (WB AMBRA1). (E) ULK1 phosphorylates AMBRA1. HEK293 cells were transfected with expression vectors encoding AMBRA1–Flag together with wild-type (Wt) ULK1 or K46I ULK1 Myc-tagged proteins. 48 h after transfection, protein extracts were prepared and subjected to WB using an anti-AMBRA1 antibody (WB AMBRA1). (F) HEK293 cells were transfected with an expression vector encoding Myc-tagged wild-type ULK1. 48 h after transfection, cells were lysed with HEMG and subjected to an in vitro λ-phosphatase assay as described in Materials and methods. After denaturation, protein extracts were subjected to WB using anti-AMBRA1 (WB AMBRA1; left) and anti-Myc (WB Myc; right) antibodies.