Figure 4.
Neutralizing Mcl-1 sensitizes different cell types to ABT-737
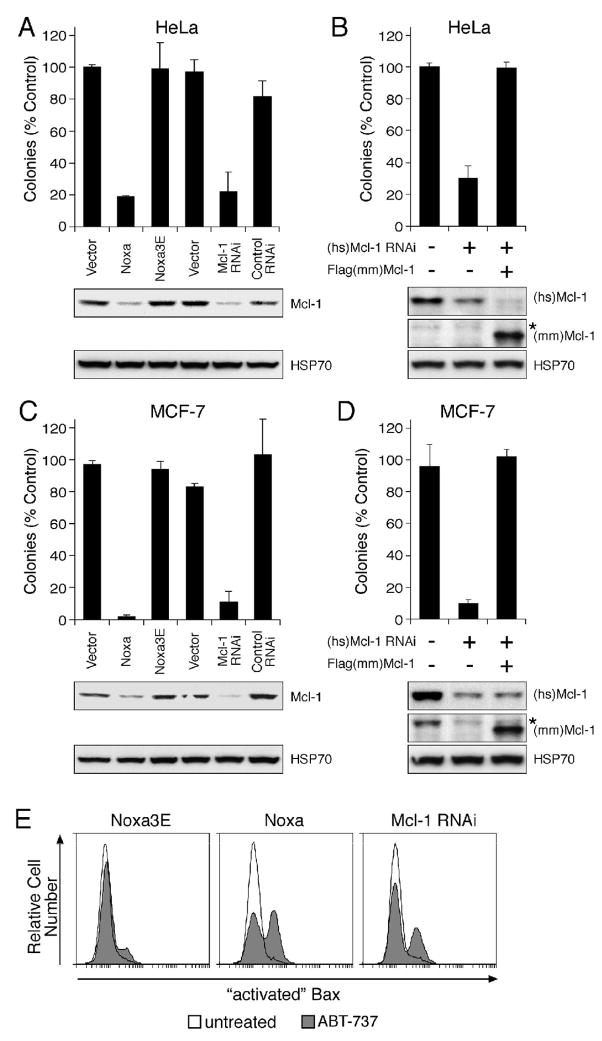
Colony formation after continuous exposure to ABT-737 (1 μM, replenished every 3 d) of HeLa (A, B) or MCF-7 cells (C, D) infected with empty vectors, or stably expressing Noxa, mutant Noxa 3E, RNAi targeting Mcl-1, or RNAi to an irrelevant target (control RNAi). Introduction of mouse Mcl-1, which is not targeted by the human specific Mcl-1 RNAi construct, restored the resistance in HeLa (B) or MCF-7 cells (D) to ABT-737. Clonogenic survival data (after 7 d) are representative means ± SD of 3 independent experiments. (A, B) The lower panels are immunoblots for Mcl-1 or HSP70 (loading control). (C, D) The lower panels are immunoblots for human Mcl-1 (top), mouse Mcl-1 (middle: * residual signal from human Mcl-1 probe) or HSP70 (lower panel).
E: ABT-737 triggers Bax activation when Mcl-1 is neutralized. HeLa cells expressing mutant Noxa 3E, Noxa or Mcl-1 RNAi, were treated for 4 h with ABT-737 (10 μM), and Bax activation detected by flow cytometric analysis after staining permeabilized cells with an antibody (clone 3) that specifically recognizes activated Bax (Willis et al., 2005).