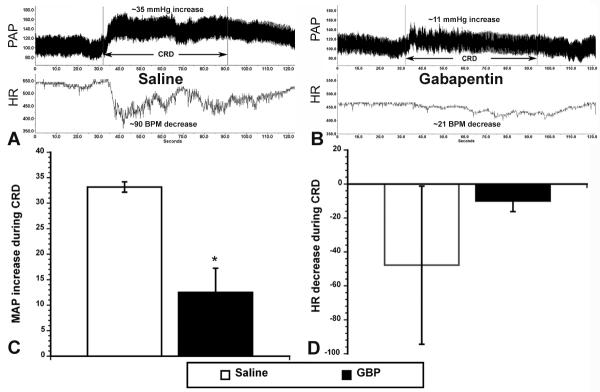
Figure 3.
Illustrative traces of pulsatile arterial pressure (PAP) and heart rate (HR), measured by telemetric probes in descending aorta before, during and after one minute of noxious colorectal distension (CRD) in (A) injured rats injected with saline versus (B) injured rats injected with gabapentin (GBP) 21 days post injury. With GBP treatment, the increased MAP and decreased HR (bradycardia) appear strikingly attenuated in response to CRD. Quantitative analysis (C) confirmed a significant reduction in CRD-induced MAP of more than two-fold with GBP treatment. While bradycardia appeared to be reduced (D), the variability precluded significant differences. *p<0.05 n=3 Saline; n=3 GBP (50 mg/kg) Bars represent mean ± SEM