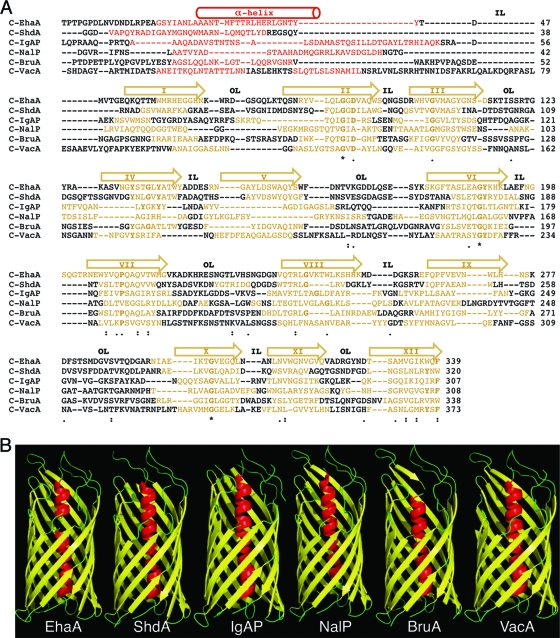
FIG. 1.
Secondary- and tertiary-structure predictions of the selected AT C-terminal domains. (A) Alignment of the amino acid sequences of the C-terminal domains of the EhaA, ShdA, IgAP, NalP, BruA, and VacA ATs. The sequence predicted by the PSI-pred program (22) to fold as a hydrophilic α-helix is represented in red. The transmembrane amphipathic β-strands predicted with the Pred-TMBB (1) and ProfTMB (4) programs are shown in yellow. For clarity, the regions adopting α-helix or β-strand structures are also indicated with a cylinder or arrows on top, respectively. The roman numerals inside the arrows indicate the numbers of the β-strand (I to XII). Predicted inner loops (IL) and outer loops (OL) are labeled. Symbols indicating identity and similarity in the sequence alignment, according to the Tcoffe server (44), are indicated: *, 100% identity; :, >60% similarity; ·, >40% similarity. The conserved amino acid residues shown in boldface type correspond to those conserved in the alignment of the autotransporter family (Pfam accession number PF03797) from the Pfam server (12). (B) 3D structures of the C-terminal domains of selected ATs obtained with the Genesilico Metaserver-meta2 server (34). The secondary and tertiary structures of C-NalP correspond to the crystal structure data for NalP (41).