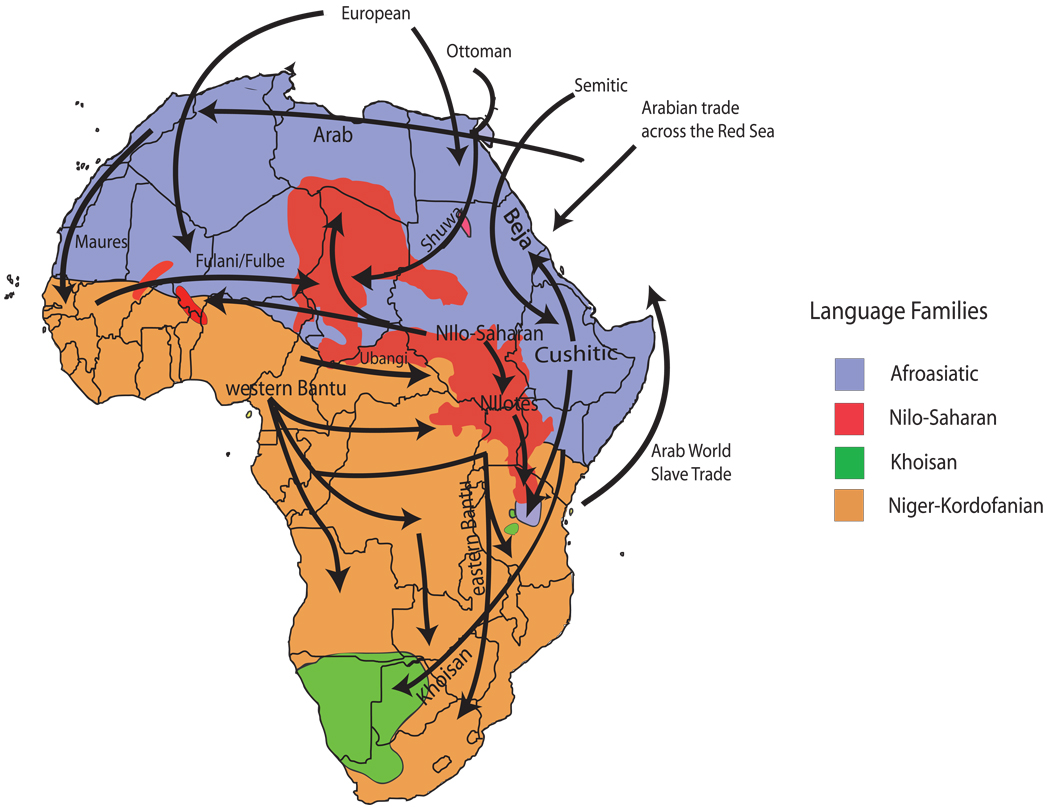
Figure 1.
A map of African language family distributions and hypothesized migration events within and out of Africa. African languages have been classified into four major language families: Niger-Kordofanian (spoken predominantly by agriculturalist populations across a broad geographic distribution in Africa), Afro-Asiatic (spoken predominantly by northern and eastern Africa pastoralists and agropastoralists), Nilo-Saharan (spoken predominantly by eastern and central African pastoralists), and Khoisan (a language containing click-consonants, spoken by southern and eastern African hunter-gatherer populations). Also plotted are the geographic origins of African samples included in the Center d’Etude du Polymorphisme Humain (CEPH) Human Genome Diversity Panel (CEPH-HGDP). Diagram adapted from Reference 170.