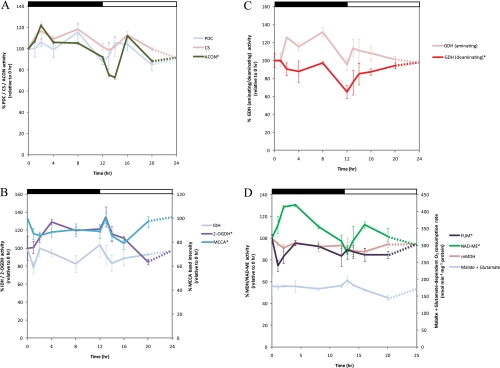
Fig. 3.
Changes in enzyme activities focused on TCA cycle, glutamate metabolism/catabolism, and branched-chain amino acid degradation in mitochondria during diurnal cycle in Arabidopsis shoot. A, changes in the activity of entry steps of the TCA cycle in the mitochondria. Enzyme activity was measured for PDC, CS, and ACON. B, changes in the activity of decarboxylating dehydrogenases in the TCA cycle and branched-chain amino acid degradation in the mitochondria. Enzyme activity was measured for IDH and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (2-OGDH). The intensity of the band containing a biotin-containing protein, MCCA, on immunoblot over a 24-h period was also plotted (also see supplemental Fig. 2A). C, changes in the activity of aminating and deaminating activity of glutamate dehydrogenase in the mitochondria. D, analysis of the TCA cycle enzymes in the mitochondria focused on malate formation and utilization. Oxygen consumption in the presence of malate + glutamate supplemented with appropriate cofactors was measured. Enzyme activity was measured for mMDH, NAD-ME, and fumarase (FUM). All data are plotted with respect to 0 h (100% activity or band intensity) with the exception of substrate-dependent oxygen consumption measurements. The catalytic activity profiles of enzymes found to be significantly changed between data points (one-way ANOVA p < 0.05) are indicated with an asterisk (*). A Tukey analysis is shown in supplemental Table 3. The results are shown as means from three biological replicates with error bar representing relative S.E. The day/night cycle is indicated at the top of the plot by a white (day) and a black (night) bar.