Figure 1.
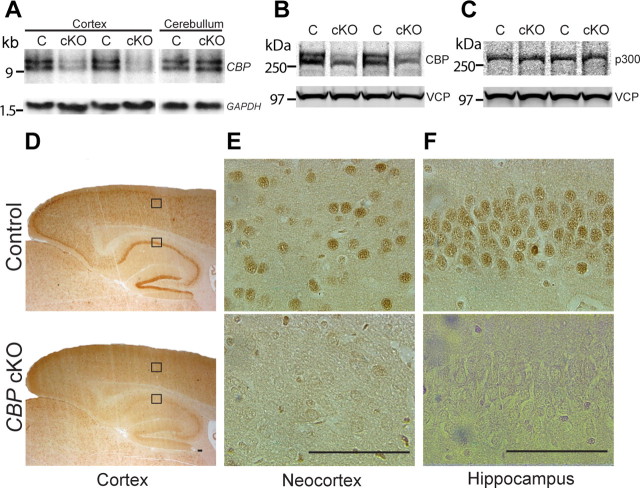
Molecular characterization of forebrain-specific CBP cKO mice. A, Northern analysis of CBP transcripts. There is a dramatic reduction on CBP mRNA levels in the cerebral cortex of CBP cKO mice (n = 3 per group, p < 0.05). There is no significant change in CBP mRNA levels in the cerebellum (p > 0.3). GAPDH serves as the internal control (C). B, Immunoblotting of CBP using cortical lysates of CBP cKO and control mice at 2 months of age. CBP protein levels are significantly reduced in CBP cKO mice (n = 5 per group, p < 0.05). Valosin-containing protein (VCP) serves as loading controls. C, Immunoblotting of p300 using cortical lysates of CBP cKO and control mice at 2 months of age. Protein levels of p300 are not significantly affected (n = 5 per group, p > 0.2). Valosin-containing protein serves as loading controls. D, Immunostaining of CBP using brain sections of control and CBP cKO mice at 2 months of age (2× magnification). A cortical inset and a hippocampal inset are enlarged in E and F. E, Immunostaining of CBP in the neocortex at 60× magnification. F, Immunostaining of CBP in the hippocampal CA1 area at 60× magnification. Scale bar, 100 μm.