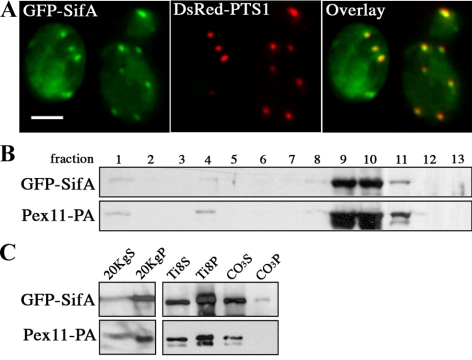
Figure 2.
SifA distributes to the peripheral membrane of peroxisomes in yeast. (A) GFP-SifA (pDV116) colocalizes with the peroxisomal reporter DsRed-PTS1 in wild-type yeast cells as indicated by yellow in the merged image. Cells containing two plasmids expressing the indicated fusion reporters were grown in media containing raffinose and then fixed and analyzed by direct fluorescence microscopy. Bar, 4 μm. (B) GFP-SifA cofractionates with the peroxisomal marker Pex11-PA by isopycnic centrifugation. Cells containing a chromosomal copy of Pex11-PA were transformed with pDV116 and induced in oleic acid for 17 h before biochemical fractionation. GFP-SifA–enriched material derived from the 20KgP crude organellar fraction (in C) was applied to a Nycodenz gradient and separated by centrifugation. Gradient fractions were collected from the top (fraction 1), and equal portions of each fraction were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-GFP and anti-pA antibodies. (C) Materials from fraction 10 were further extracted in a low-salt buffer to separate matrix (Ti8S) from membrane (Ti8P) peroxisomal proteins. The Ti8P fraction was again extracted with Na2CO3 to distinguish between peripheral membrane (CO3S) and integral membrane (CO3P) proteins. Equivalent portions of each fraction were analyzed by Western blot. Note that GFP-SifA and Pex11-PA behave mainly as peripheral membrane proteins.