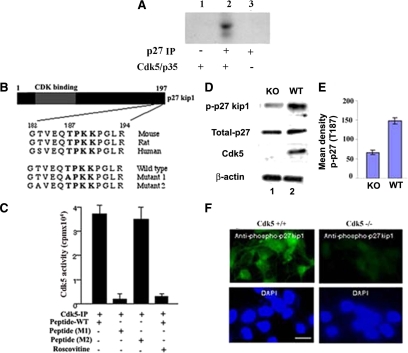
Figure 5.
Phosphorylation of p27Kip1 and analysis of peptides derived from p27Kip1 to identify the potential site phosphorylated by Cdk5. (A) Phosphorylation of p27Kip1 by Cdk5. In the absence of recombinant p27Kip1, we used a p27Kip1 immunoprecipitation (IP) of E16 brain lysate as substrate for a Cdk5 kinase assay. The radioautograph shows that p27Kip1 is phosphorylated by the active Cdk5/p35 complex. (B) A diagram of the p27Kip1 protein sequence is shown with its Cdk5-binding domain at the N-terminus. Below, a Cdk5 consensus sequence is shown within conserved residues 182-194 of p27Kip1 from mouse, rat, and human. Thr187 in p27Kip1 occupies a Cdk5 consensus motif, TPKK. Two mutants were constructed as shown: mutant 1 with alanine replacing threonine 187 and mutant 2 with an alanine substitution at threonine 183 as a control. (C) The Cdk5+/+ and mutant peptides were used as substrates in vitro kinase assays using Cdk5 immunoprecipitated from brain lysates. The bar graph, based on three experiments, shows the control mutant 2 (183A) exhibited a level of phosphorylation comparable to a wild-type (WT) peptide, whereas mutant 1 (187A) showed activity equivalent to the roscovitine-inhibited activity of the WT peptide. (D) Western blots of lysates from E16 Cdk5+/+ and Cdk5−/− cultured cortical neurons were probed with antibodies to p27Kip1 and a specific phospho-p27Kip1, phosphorylated at Thr187. Compared with the WT, a reduced expression of phospho-p27Kip1 (approximately one-third, as indicated in the bar graph, n = 3) could be detected in the Cdk5−/− lysates, although the expression of total p27Kip1 was equivalent in both. (E) Densitometry analysis of p-p27(T187) from Cdk5+/+ and Cdk5−/− cultured cortical neurons (F) Immunocytochemical assays of cortical neurons using the phospho-Thr187-p27Kip1 antibody to confirm the absence of expression in the Cdk5−/− neurons compared with Cdk5+/+ neurons. Bar, 10 μm.