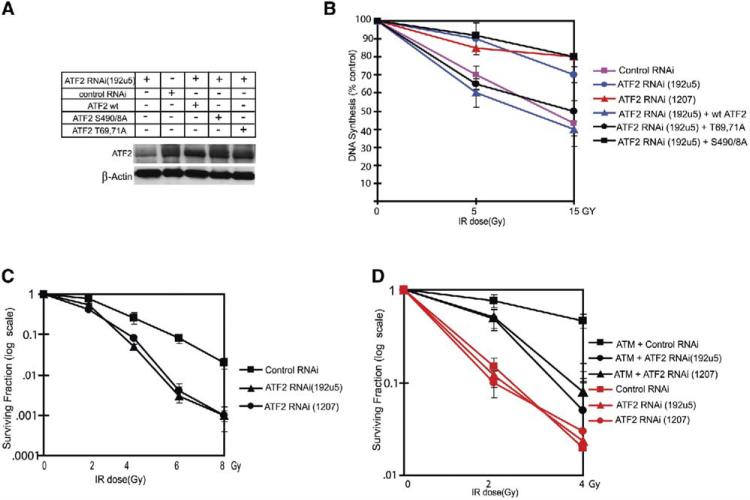
Figure 4. ATF2 Is Required for Checkpoint Control and Resistance to IR.
(A) Mutant ATF2 forms expressed at levels of endogenous ATF2. Wild-type, transcriptionally inactive (T69, 71A), and ATM phosphomutant (S490 and 498A) forms of ATF2 were transfected into MeWo cells after inhibiting endogenous ATF2 expression with RNAi to achieve expression levels equivalent to that of endogenous ATF2 (transfection efficiency = 65%). Immunoblot analysis using ATF2 antibodies was carried out 36 hr after transfection. These conditions were used throughout the related experiments.
(B) ATF2 is required for inhibition of DNA synthesis after IR. MeWo cells were infected with ATF2-RNAi (192U5, which targets 5# UTR) followed by transfection of empty vector or ATF2 forms. DNA synthesis was monitored using 14C followed by 3H-thymidine labeling. Change in the percent of DNA synthesis is shown based on five independent experiments 45 min after treatment with IR (5 Gy or 15 Gy). Calculation is based on the ratios of [3H]:[14C] and expressed DNA synthesis, which was normalized to control values (0 Gy) for every individual sample (pSuper, ATF2 RNAi, and the like). Data shown reflect triplicate measurements carried out in three experiments, which were used for calculating standard deviation as reflected in error bars.
(C) ATF2 affects cell radiosensitivity. Sensitivity to IR was determined by the colony formation assay in U2OS cells infected with control or two different ATF2 RNAi (Figure S4A; 192U5 and 1207). Surviving fraction is plotted as log of colonies after IR/colonies without IR. Error bars reflect standard deviations of triplicate samples for each point based on three experiments.
(D) ATM is required for ATF2-dependent radioresistance. A-T cells and A-T cells reconstituted with ATM (4000 cells per 60 mm plate) were subjected to IR at the indicated doses, and CFE were counted 18 days later. Cells were also subjected to infection with two different ATF2 or a control RNAi, to determine the role of ATF2 in radioresistance in A-T cells. The surviving fractions were plotted by calculating the log of colonies after IR/colonies without IR. Error bars reflect standard deviation based on triplicate analysis.