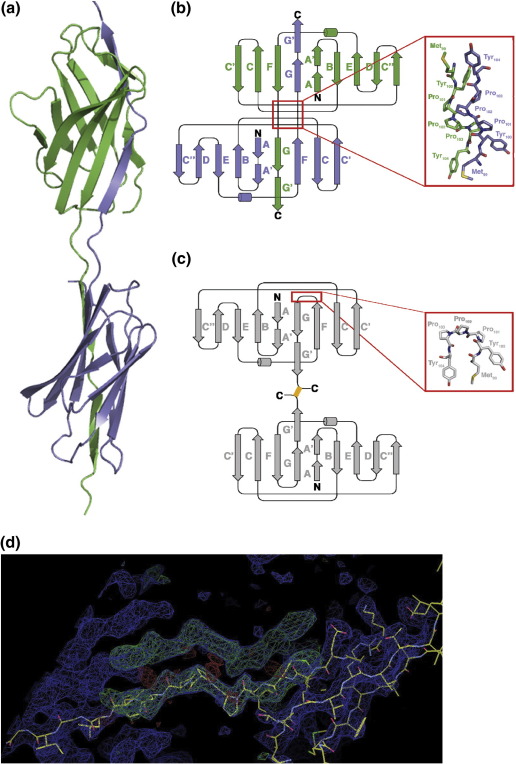
Fig. 1.
Structure of a strand-swapped Ig-domain dimer. The structure of the stand-swapped dimer is shown in (a) and its topological diagram in (b) (strands named according to standard conventions). For comparison, (c) displays the topology diagram of the homodimeric maCTLA-4 ectodomain (Yu et al., manuscript in preparation). The location of the disulfide is shown in yellow. The close-ups are molecular representations of the hinge regions (red boxes) in the swapped (top, carbon in green, oxygen in red, nitrogen in blue and sulfur in yellow) and unswapped (bottom, same colours except carbon in grey) vl-Ig domains. For purification of samples, see Supplementary Fig. S1 and Ref. 19; for structure determination method and statistics for ecCTLA-4, see Table 1. (d) Omit map calculations for the structure. The hinge region of the dimer was omitted in calculation of both the 2Fo − Fc map (blue) and the Fo − Fc map (green, at + 3σ; red at − 3σ). The atomic model for one-half of the crystallographic dimer is included in the figure.