Figure 9.
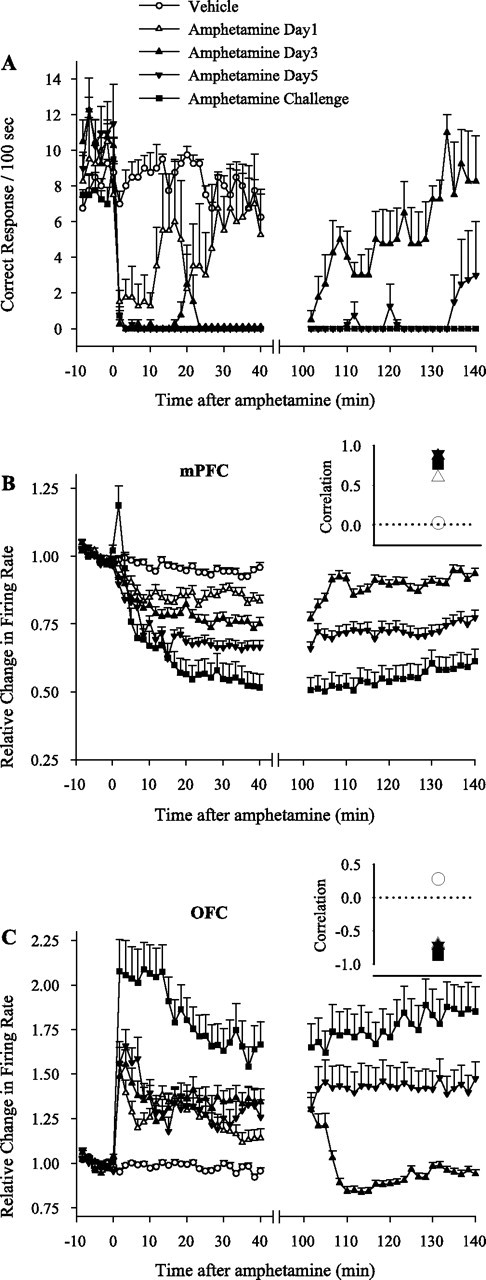
Behavioral and neuronal responses to amphetamine during instrumental responding task. A, Temporal profile of average ± SEM instrumental responses during each treatment session. Each animal was run on a 10 min baseline instrumental responding task (FR1), followed by injection of vehicle or amphetamine (2 mg/kg) and 40 min of post-injection instrumental responding. Whenever drug treatment caused severe behavioral impairment (days 3, 5, and challenge), an additional 40 min run was allowed at 100–140 min after injection. Amphetamine caused a significant impairment in behavioral responding compared with vehicle (repeated measures two-way ANOVA; from minutes −10 to 40; treatment, F(4,15) = 17.61, p < 0.001; time, F(29,435) = 38.31, p < 0.001; treatment × time interaction, F(116,435) = 4.37, p < 0.001). The impairment was partial on day 1 but complete on days 3, 5, and challenge (significantly stronger than day 1 based on pairwise group comparisons with two-way ANOVA). In addition, behavioral responding was recovered during the late run on day 3 but not on days 5 or challenge (two-way ANOVA; from minutes −10 to 0 plus minutes 100 to 140; F(2,9) = 51.69, p < 0.001; time, F(29,261) = 24.5, p < 0.001; treatment × time interaction, F(58,261) = 2.03, p < 0.05). The y-axis shows the number of delivered food pellets during each 100 s bin. B, C, Average normalized firing rates of all mPFC (B) or OFC (C) neurons recorded simultaneously with instrumental responding during each treatment day. Amphetamine treatment decreased the average firing rate in mPFC (two-way ANOVA with time as repeated measure; from minutes −10 to 40; treatment, F(4,518) = 23.73, p < 0.001; time, F(29,14993) = 205.41, p < 0.001; treatment × time interaction, F(116,14993) = 19.80, p < 0.001) and increased it in OFC (treatment, F(4,413) = 19.55, p < 0.001; time, F(29,11977) = 79.44, p < 0.001; treatment × time interaction, F(116,11977) = 13.72, p < 0.001). The mPFC inhibition was significantly stronger on days 3, 5, and challenge compared with day 1 and on challenge day compared with day 5 (pairwise two-way ANOVAs). The OFC excitation during post-injection run was not different between days 1, 3, or 5 but was stronger on challenge day compared with day 1 (pairwise two-way ANOVAs). In both regions, response to amphetamine challenge during the late run was significantly stronger than the response to day 3. B, C, Insets, Coefficients of correlations between average behavioral responding and average firing rates of mPFC (B, inset) or OFC (C, inset) neurons during each treatment day. Instrumental responding was positively correlated with mPFC activity and negatively correlated with OFC activity during all amphetamine treatment days. Dotted line at 0 indicates no correlation.
