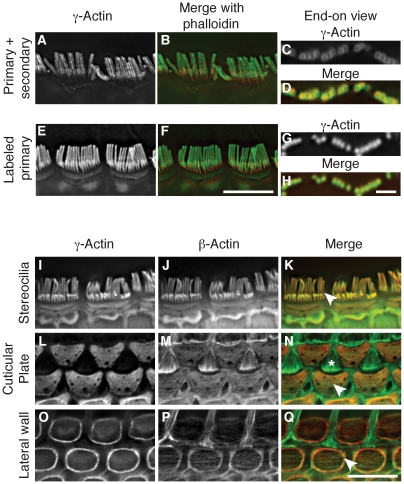
Figure 2. β-actin and γ-actin colocalize in hair cells.
(A–H) Comparison of γ-actin localization using unlabeled anti-γ-actin antibody with a fluorescent secondary antibody (A–D) or using the same anti-γ-actin antibody coupled directly to a fluorescent dye (E–H). Detection with a secondary antibody results in a peripheral localization pattern when viewed laterally (A–B) or end-on (C–D). Dye-conjugated anti-γ-actin antibody labels stereocilia uniformly and completely overlays with phalloidin in lateral (E–F) or end-on (G–H) views. In merged images, γ-actin is green and phalloidin is red. (I–Q) Localization of β-actin and γ-actin using primary antibodies conjugated to two different fluorescent dyes. γ-Actin and β-actin colocalize in stereocilia (I–K), cuticular plate (L–N) and lateral wall (O–Q). In merged images, β-actin is green and γ-actin is red. Arrowheads indicate the structure of interest and the asterisk in (N) marks the top of a support cell that borders outer hair cells. Bars in F and Q, 5 µm; H, 2 µm.