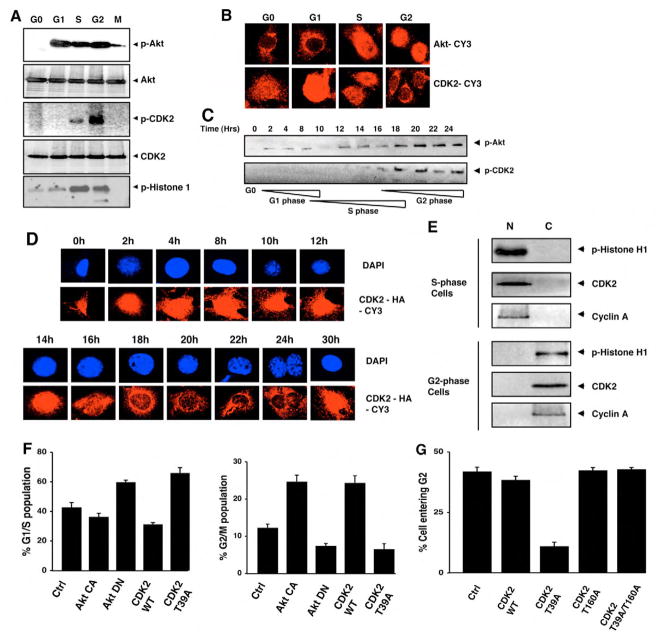
Fig. 3.
Akt-regulated CDK2 relocalization is required for cell cycle progression. (A) Murine 3T3 fibroblasts were arrested in G0, G1, S, G2 and M phases of the cell cycle, as described in the Materials and Methods section, and the phosphorylated Akt, total Akt, phosphorylated CDK2 and total CDK2 were detected by immunoblotting with their respective antibodies. The CDK2 kinase activity is shown at different phases of the cell cycle using histone H1 as substrate. (B) The 3T3 fibroblasts were arrested in different phases of the cell cycle and the localization of Akt was detected by using confocal microscopy after immunostaining with Akt antibody followed by Cy3-conjugated secondary antibody (upper panel). In parallel samples, the localization of CDK2 was detected by using CDK2 antibody followed by Cy-3 conjugated secondary antibody (lower panel). (C) 3T3 fibroblasts were serum-starved for 36 hours and then serum was added to allow the cells to progress sequentially through different phases of the cell cycle. At the indicated time points, cells were sampled, the phosphorylated Akt was detected by immunoblotting and the phosphorylated CDK2 was detected by immunoprecipitation of CDK2 followed by immunoblotting with anti-phospho-substrate-Akt antibody. The stages of the cell cycle were confirmed by ‘FITC-BrdU Flow Kit’ staining, followed by flow cytometry at the indicated time points; each cell cycle phase is denoted below the lower immunoblotting panel. (D) The cells grown on coverslips were synchronically put through the cell cycle as described above; they were then collected at indicated time points, and the localization of CDK2 was detected by confocal microscopy preceded by immunostaining with anti-CDK2 antibodies followed by a Cy-3 conjugated secondary antibody. DAPI is used to counterstain the nucleus. (E) The nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) fractions from 3T3 fibroblasts synchronized in either S phase or in G2 phase were isolated and the CDK2 kinase activity measured using histone H1 as substrate after immunoprecipitating with CDK2 antibodies. The presence of CDK2 and cyclin A were also detected in both the fractions using their respective antibodies. (F) 3T3 fibroblasts were transfected with Akt-CA, Akt-DN, wild-type CDK2, or with CDK2-T39A-expressing vectors. Twenty-four hours later the percentage of G1-S and G2-M population was gated and analyzed by flow cytometry following propidium iodide staining. (G) The cells were transfected with wild-type CDK2-, CDK2-T39A-, CDK2-T160A- or CDK2-T39A/T160A-expressing vectors, then arrested in S phase using 2 μg/ml aphidicolin for 20 hours and released from S phase for 3 hours. The percentage of cells moving from S to G2 phase was assessed by BrdU labeling, as described in the Materials and Methods section, followed by flow cytometric analysis.