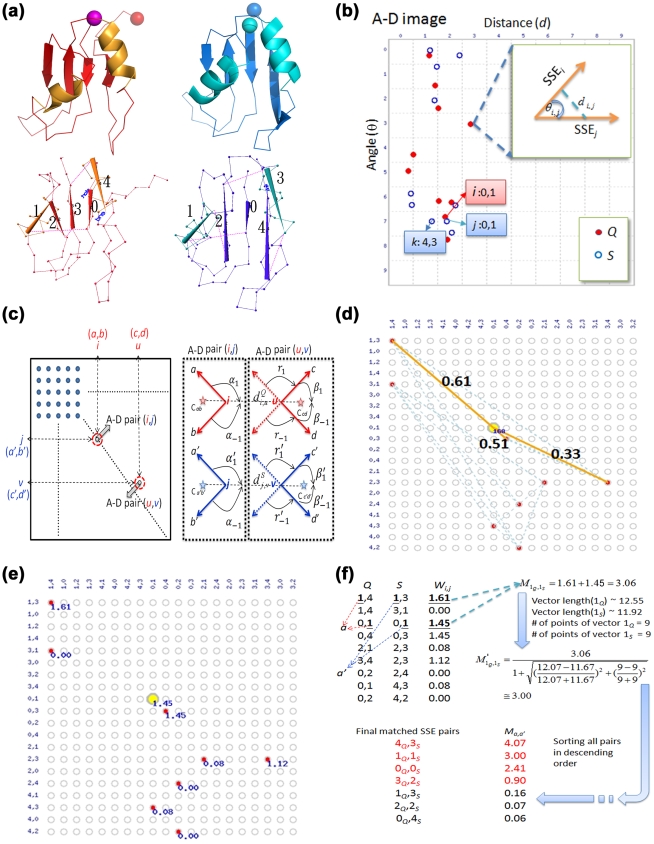
Figure 5. A-D image-based SSE matching.
(a) RNA binding domains 2u2fA (red; Q) and 1no8A (blue; S) and their corresponding vectorized SSEs. (b) After transforming these structures into A-D images, in which each point comprised two SSEs [38], the A-D images were virtually superimposed and compared to find probable inter-image pairings between A-D points from the two images. Take the point i from Q for instance; it could be paired with its nearby points j and k from S. (c) Each probable pair of points, such as (i, j), was allowed to form a vertex in the pair-graph. Then, a delicate scoring scheme was applied to determine the geometric similarity between vertices. As illustrated here, many distances and angles of the component SSEs of two vertices were incorporated in this scheme (see the main text for details). (d) An edge (yellow line) was formed between two vertices sharing a positive score. (e) A weight was thus assigned to a vertex by summing the scores of the edges associated with the vertex. For example, the weight of the central yellow vertex was 1.45, i.e., 0.61+0.51+0.33. (f) In the last stage, for every SSE pair (a, a′), where a is from Q and a′ from S, a matching score 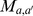 was assigned to it as the summation of all weights of the vertices associated with both a and a′. In this example, because a = 1Q and a′ = 1S, the scores of the rows possessing both 1Q and 1S were summed to yield
was assigned to it as the summation of all weights of the vertices associated with both a and a′. In this example, because a = 1Q and a′ = 1S, the scores of the rows possessing both 1Q and 1S were summed to yield 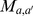 = 3.06.
= 3.06. 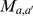 was then refined by a weighting function to become
was then refined by a weighting function to become 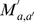 . After sorting all SSE pairs according to
. After sorting all SSE pairs according to 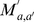 in a descending order, the first SSE pair was treated as the first matched SSE pair to identify the successive matched SSE pairs as described in the main text.
in a descending order, the first SSE pair was treated as the first matched SSE pair to identify the successive matched SSE pairs as described in the main text.