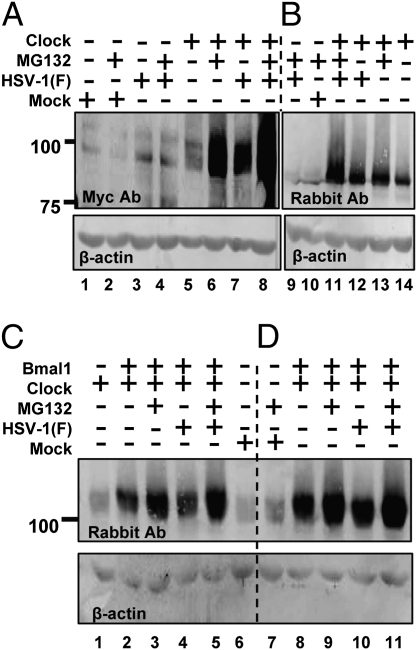
Fig. 3.
HSV-1(F) stabilizes the exogenous CLOCK. (A and B) Vero cells were exposed to 10 pfu of HSV-1(F) per cell 24 h after transfection of a plasmid encoding myc–CLOCK. MG132 (5 μM) was added to the cultures 2 h after infection. The cells were harvested at 9 h after infection, and equal amounts of cellular proteins were analyzed for the abundance of the CLOCK either with the myc antibody (A) or with the CLOCK antibody (B). (C and D) Vero cells transfected either with the expressing myc–CLOCK only or cotransfected with plasmids encoding myc–CLOCK and HA–Bmal1 were infected with the HSV-1(F) virus and/or treated with MG132 as above. The cells were harvested at 4 or 9 h after infection. The electrophoretically separated proteins were immunoblotted with a CLOCK antibody. In all panels β-actin served as a loading control.