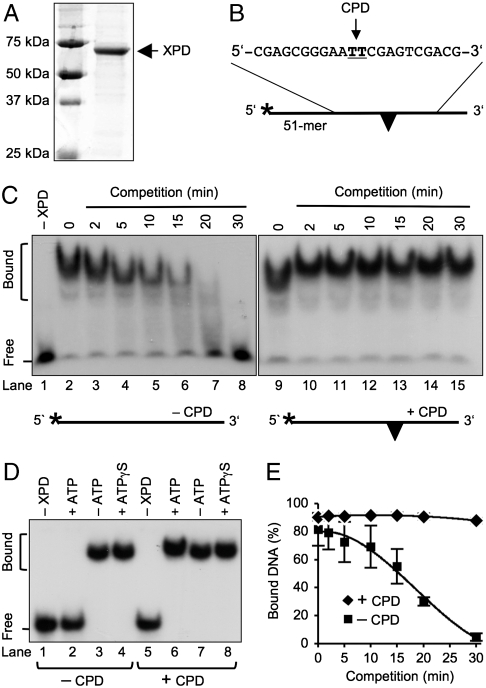
Fig. 2.
Immobilization of the XPD enzyme. (A) Electrophoretic analysis and Coomassie staining of FaXPD protein. (B) Oligonucleotide used for competition assays. The CPD is indicated by a triangle and the 32P label by an asterisk. (C) Competition in the presence of 3 mM ATP showing the dissociation of FaXPD from undamaged oligomers (lanes 3–8) and the stability of radiolabeled complexes containing a single CPD (lanes 10–15). Competitor DNA (undamaged 51-mer) was added in a 50-fold excess. Lanes: 1, incubation without protein; 2 and 9, control incubations (60 nM FaXPD and 5 nM radiolabeled oligonucleotides) without competitor DNA. F, free probes; B, protein-bound fraction. (D) ATP-dependent dissociation of FaXPD from undamaged oligonucleotides. Lanes: 4 and 8, competition assays with nonhydrolyzable ATPγS. (E) Quantification of competition assays. FaXPD (60 nM) was incubated (15 min) with radiolabeled 51-mers (5 nM). A 50-fold molar excess of unlabeled 51-mers was then added in the presence of 3 mM ATP and, after varying competition periods, the samples were analyzed in mobility shift gels. The fraction of protein-bound DNA is represented as the percentage of total radioactivity (N = 3; ± SD).