Figure 5. Integrative method increases methylome coverage and enables identification of a DMR.
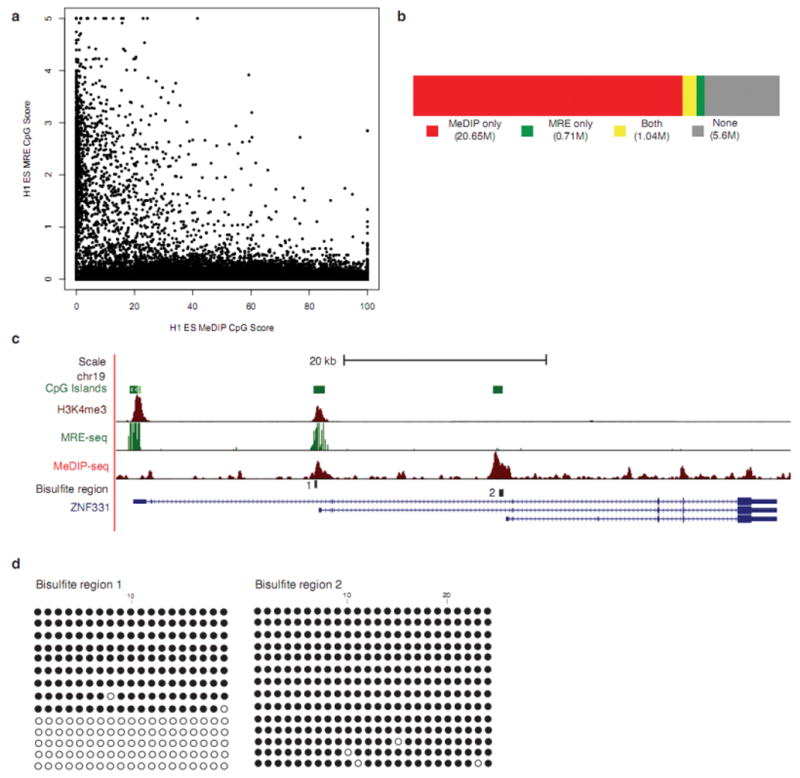
(a) MRE-seq involves parallel digests with methylation sensitive restriction enzymes (HpaII, AciI, and Hin6I), selection of cut fragments of approximately 50bp–300bp, pooling the digests, library construction, and sequencing. For every 600bp window along chromosome 21, MeDIP-seq scores were plotted against MRE-seq scores. The plot depicts the inverse relationship between MRE-seq and Me-DIP-seq signals. (b) Coverage of CpGs in the human genome by MeDIP-seq alone (red), MRE-seq alone (green), both (yellow), or neither method (no fill). Sequence from replicate #1 and #2 were used in these calculations (c) UCSC Genome Browser view of ZNF331in H1 ESC, showing overlap of Me-DIP-seq, MRE-seq and H3K4me3 (from ChIP-seq) signals at bisulfite region 1 and only MeDIP-seq signal at bisulfite region 2. (d) Clonal bisulfite sequencing results for specified regions in ESC from replicate #1. A filled circle represents a methylated CpG and an open circle indicates an unmethylated CpG.
