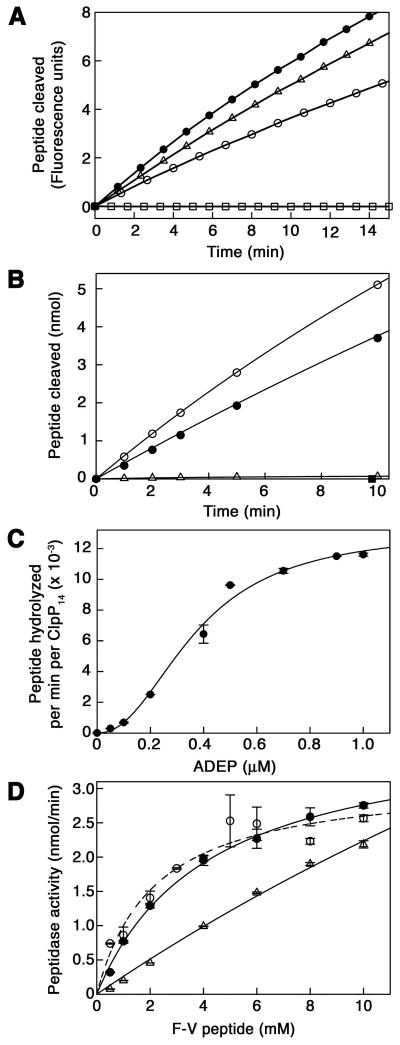
Figure 2. Kinetic Parameters for ADEP Activation of ClpP Peptidase Activity.
(A) Time course of hydrolysis of the fluorogenic peptide N-Succinyl-Leu-Tyr-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin (0.2 mM) by E. coli ClpP (50 μg/ml) in the presence (open circles) and absence (closed circles) of 10 μM ADEP1. Control reactions containing the fluorogenic peptide and ADEP1 but not ClpP (open squares) or ClpP with equivalent amounts of DMSO (open triangles) are also shown. (Arbitrary fluorescence units reflect release of aminomethylcoumarin). See also Supplemental Table 1.
(B) Time course of cleavage of the 10-residue peptide, F-V (1 mM), by ClpP (1 μg/ml) in the presence (open circles) and absence (open triangles) of 10 μM ADEP1. Peptide products released were quantitated by absorbance measurements after reverse phase chromatography. For comparison, ClpP peptidase activity stimulated by ClpA (10 μg/ml) in the presence of 1 mM ATPγS was also measured (closed circles). A control reaction containing only F-V and ADEP1 is also shown (closed squares). See also Supplemental Table 1.
(C) Dependence of ClpP activation on ADEP1 concentration. ClpP (1.0 μg/ml) and F-V (2 mM) were held constant and the concentration of ADEP1 added was varied. Results are the average of two separate experiments.
(D) Substrate-dependence of ClpP peptidase activity in the presence of 10 μM ADEP1 (open circles). ClpP (1.0 μg/ml) and ADEP1 (10 μM) were held constant and the concentration of F-V was varied. For comparison, the substrate-dependence was measured for F-V cleavage by ClpAP (1.0 μg/ml ClpP, 10 μg/ml ClpA) (closed circles) and by ClpP alone (10 μg/ml) (open triangles), which showed no sign of saturation at the highest concentrations used. Results are the average of two separate experiments. Note that the activity with ClpP alone is ~2% of the activity with ADEP1 present.