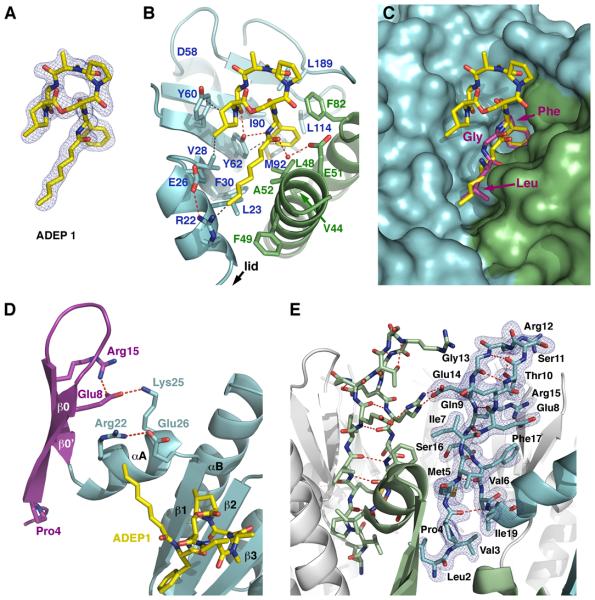
Figure 5. Binding Interactions of ClpP with ADEP1 and Organization of the N-terminal Loops in the ClpP-ADEP1 structure.
(A) Final model of ADEP1 shown as color-coded sticks with the 2|Fo|-|Fc| electron density map contoured at 1.0 σ level.
(B) Detailed interactions between ADEP1 and the residues defining the hydrophobic pocket in ClpP. Adjacent ClpP monomers are shown as ribbon diagrams in light blue and green, with interacting side chains depicted as color-coded sticks and labeled. Hydrogen bonds (red) and van der Waals interactions (grey) are shown as dashed lines.
(C) Superimposition of the conserved LGF motif (consensus sequence IGF) from Helicobacter pylori ClpX (purple color-coded sticks) onto the structure of ClpP bound to ADEP1 shown in the same orientation and color scheme as in (B).
(D) Ribbon diagram of a ClpP monomer with the N-terminal region shown in purple and the head domain shown in light blue. Side chains of residues involved in anchoring the N-terminal lid to the head domain are shown as sticks with the hydrogen bonds depicted as dashed lines (red). ADEP1 is shown as yellow color-coded sticks.
(E) Ribbon diagram of the ClpP heptamer with two adjacent monomers shown in light green and blue, while the rest are shown in white. Two N-terminal lids (residues 1-19) are shown as sticks, with the intra- and inter-molecular hydrogen bonds maintaining the β-hairpin structure depicted as red dash lines. The 2|Fo|-|Fc| electron density map around one of the lids is shown in blue and contoured at 1.0 σ level.