Figure 3. CAND-1 negatively regulates CUL-2 and CUL-4 neddylated isoform levels.
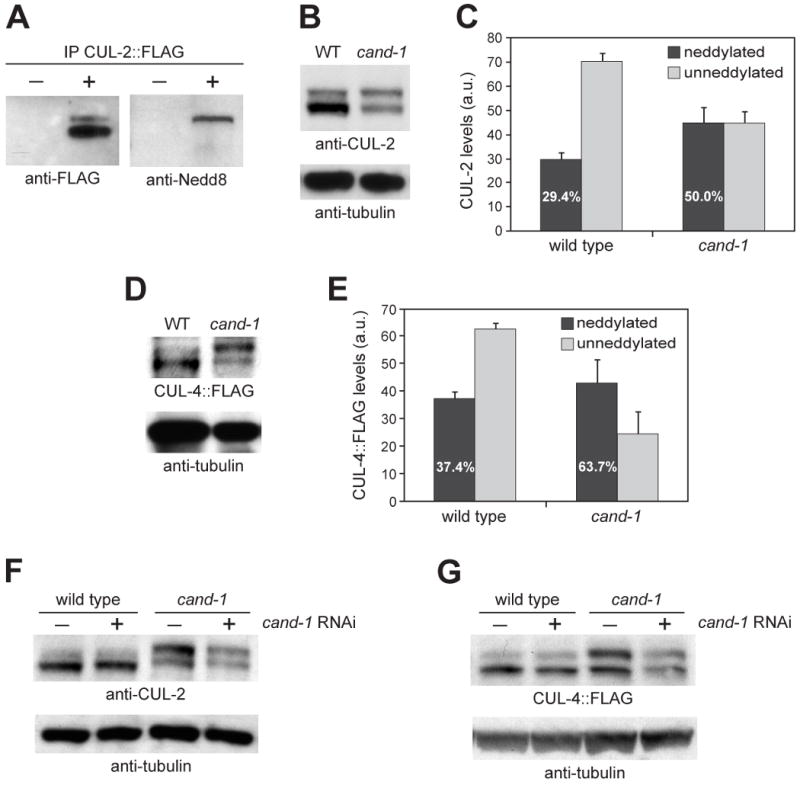
(A) Anti-FLAG immunoprecipitation from wild type (-) or animals expressing CUL-2∷FLAG (+), probed by Western blot with anti-FLAG and anti-Nedd8 antibodies. (B) Whole-worm lysates from wild type and cand-1 mutants blotted with anti-CUL-2 and anti-tubulin antibodies. (C) Graph of the average level of covalently-modified (neddylated) or unneddylated CUL-2 isoforms in wild type and cand-1 mutants from nine independent experiments. The levels of CUL-2 isoforms in cand-1 mutants are normalized to the total CUL-2 signal of wild-type animals, which is set to 100 arbitrary units (a.u.). The percentage of CUL-2 that is in the neddylated isoform relative to the total CUL-2 within a genotype is provided in white lettering within the neddylated isoform bar. This percentage is significantly different between wild type and cand-1 mutants (p < 0.0001, n=9; Student's T-test). (D) Whole-worm lysates prepared from wild type and cand-1 mutants expressing CUL-4∷FLAG and probed with anti-FLAG and anti-tubulin antibodies. (E) Graph of the average covalently-modified (neddylated) and unneddylated CUL-4∷FLAG isoforms in wild type and cand-1 mutants from seven independent experiments. Normalization and labeling are as in (C). The percentage of the neddylated CUL-4∷FLAG isoform is significantly different between wild type and cand-1 mutants (p < 0.0005, n=7). (F) Whole-worm lysates from wild type and cand-1 mutants with (+) or without (-) cand-1 RNAi, probed with anti-CUL-2 and anti-tubulin antibodies. (G) Whole worm lysates from wild type and cand-1 mutants expressing CUL-4∷FLAG with or without cand-1 RNAi, probed with anti-FLAG and anti-tubulin antibodies.
