Table 1.
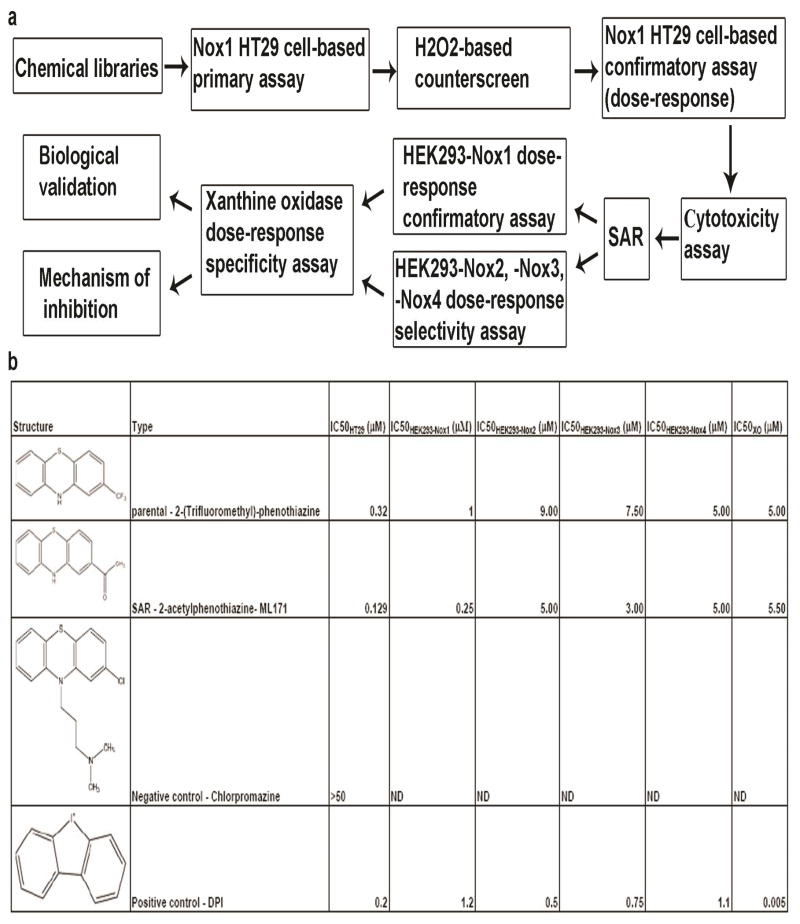
Schematic representation of the screening cascade and table summarizing IC50 values of 2-(trifluoromethyl)-phenothiazine (parental hit), ML171 (after-SAR hit), chlorpromazione (negative control) and DPI (positive control) are reported. (a) A schematic representation of screening cascade for the identification of novel Nox1 inhibitor is illustrated. Compounds which efficiently blocked light emission in our primary assay were counterscreened via i) H2O2-based counterscreen and ii) cytotoxicity assay. Hits were validated in different cell systems (HEK293-Nox1, -Nox2, -Nox3 and -Nox4) for their ability to selectively block Nox1-dependent ROS generation. Selective hits were tested for their ability to non-specifically interfere with XO-dependent ROS formation. Remaining hits were further validated as Nox1 inhibitors in biological systems and their mechanism of action was investigated. (b) IC50 values of 2-(trifluoromethyl)-phenothiazine (parental hit), ML171 (after-SAR hit), chlorpromazine (negative control) and DPI (positive control) are reported from our primary assay (IC50HT29), HEK293-Nox1 confirmatory assay (IC50HEK293-Nox1), HEK293-Nox2, -Nox3, -Nox4 selectivity assay (IC50HEK293-Nox2, IC50HEK293-Nox3 and IC50HEK293-Nox4) and Xanthine oxidase specificity assay (IC50XO).
 |
