Figure 1.
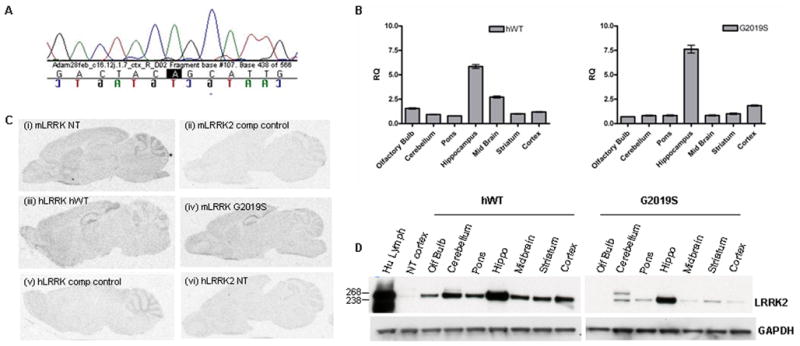
(A) Confirmation that transgenic mRNA contains the G2019S mutation. RNA was extracted from F1 G2019S transgenic mouse brain, cDNA synthesized and sequencing with human specific primers to LRRK2 exon 41 performed (the G to A transition highlighted in black).
(B) Real time PCR to examine regional expression of human mRNA expression in transgenic mice. Real-time PCR was performed with ABI (gene human LRRK2 specific TaqMan® probe Hs00417273_ml using mouse GAPDH (Mm99999915_ml) as the endogenous reference gene. Data is plotted as mean ± SEM.
(C) In situ hybridization reveals resemblance between endogenous murine LRRK2 expression and transgenic expression. (i) Murine LRRK2 was visualized with a probe to mouse exon 15 in NT mice. (ii) Excess unlabeled probe was used as control. (iii) Human LRRK2 in hWT (iv) G2019S mice was visualized with a probe to human exon 41. (v) Excess unlabeled exon 41 probe on transgenic mouse section was used as an additional control. (vi) Specificity of the human probe was confirmed by the absence of signal in NT mice.
(D) hWT and G2019S transgenic mice expression human Lrrk2 protein in multiple brain regions. Human Lrrk2 transgenic protein expression in the hWT line and the highest expressing G2019S line was evident throughout the mouse brain. 50μg of protein lysate was loaded per sample and following electrophoresis, membranes were immunoblotted with antibody PA0362. Human lymphoblast was used as a positive control. GAPDH antibody was used as a loading control.
