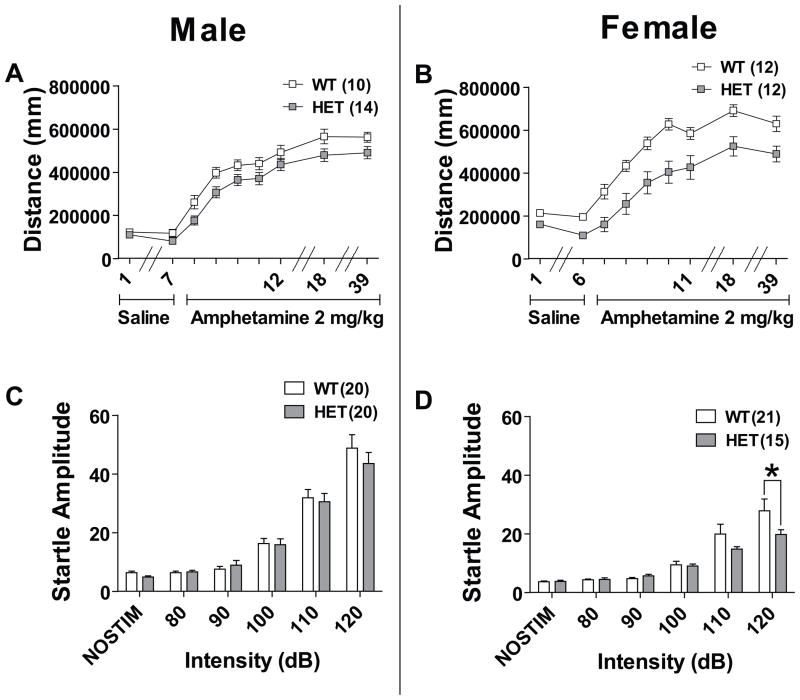
Figure 3. Effect of Cacna1c HET knockout on response to d-amphetamine and acoustic startle response.
(a) Male WT and HET mice habituated at the same level of locomotion during saline injection days 1–7. There was a significant effect of genotype to modify sensitization to d-amphetamine over days 8–12 in male mice (P<0.05). In males there was a trend for an effect of genotype to modify long-term sensitization to d-amphetamine on day 39 (P=0.063) but not day 18. (b) Female HET mice had lower locomotion during the saline habituation phase days 1–6 (P<0.001). In female HET mice there was a significant effect of genotype on sensitization to d-amphetamine (P<0.001). There remained a significant effect of genotype when females were re-challenged with d-amphetamine sensitization days 18 and 39 (P<0.001). (c) Male HET mice had no significant difference in response to multiple acoustic startle intensities. (d) Female HET mice had significantly lower acoustic startle response at 120dB. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *, P≤0.05 Bonferroni posttest.