Table 1.
Predicted helical protein-protein interactions as targets for synthetic ligands.
| PDB code, interface chains; candidate helixa | ΔΔGavg/helix (kcal/mol)b | Helix contributionc | Hot spot residue helix positiond | Chain name/Functione |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Examples of Interfaces with Binding Clefts | ||||
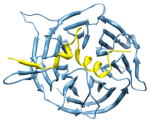 2i3s, c d; d |
2.8 | 55% | i | c: Cell cycle arrest protein |
| i + 1 | d: Checkpoint serine/threonine-protein kinase | |||
| i + 3 | Function: cell cycle | |||
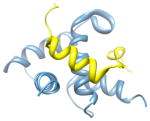 22ka6, a b; b |
2.6 | 54% | i | a: CREB-binding protein |
|
i + 1 i + 3 |
b: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1-α/β | |||
| i + 4 | Function: transcription and gene regulation | |||
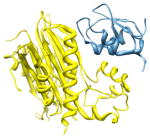 2pop, c d; c |
2.3 | 100% | i | c: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7- interacting protein 1 |
| i + 1 | d: Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein | |||
| i + 4 | Function: signaling | |||
| Examples of Extended Interfaces | ||||
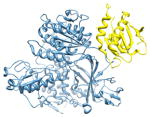 2nup, b c; c |
2.5 | 72% | i | b: Protein transport protein Sec24A |
|
i + 4 i + 5 |
c: Vesicle-trafficking protein SEC22b | |||
| i + 8 | Function: protein transport | |||
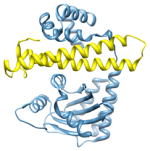 2q0o, a c; c |
2.4 | 66% | i | a: Probable transcriptional activator protein traR |
|
i + 10 i + 13 |
c: Probable transcriptional repressor tram | |||
| i + 14 | Function: transcription and gene regulation | |||
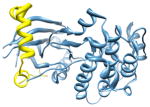 2vgo, a d; d |
2.5 | 24% | a: Serine/threonine-protein kinase 12-A | |
| i | d: Inner centromere protein A | |||
| i + 8 | Function: enzyme (transferase) | |||
Chains in the complex featuring a helix at the interface; candidate helix to be mimicked is part of the indicated chain.
ΔΔGavg/helix is derived from Rosetta computational alanine mutagenesis studies and indicates the average free energy penalty for mutating two or more key residues at the interface to alanine.
Helix contribution refers to the proportion of key contact residues positioned on the candidate helix as compared to the chain (see text for a detailed explanation).
Relative positioning of the hot spot residues on a helix.
Description of chains featuring the helical interface and cellular function.
