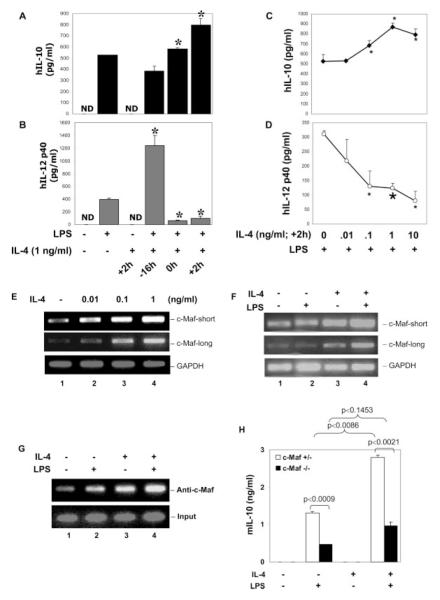
FIGURE 7.
Modulation of LPS-induced IL-10, IL-12 p40, and c-Maf expression by IL-4. A and B, Primary human monocytes were treated with LPS (1 μg/ ml) alone or recombinant human IL (hIL)-4 (1 ng/ml at +2 h) alone or LPS plus IL-4 added at different times relative to LPS. Twelve hours later, cell culture supernatants were collected for IL-10 (A) or IL-12 p40 (B) production by ELISA. *, A value of p < 0.05 compared with LPS treatment alone. C and D, Human monocytes were treated with different doses of rhIL-4 and added 2 h after LPS stimulation. Cell culture supernatants were collected 12 h after LPS stimulation for IL-10 and IL-12 p40 secretion by ELISA. *, A value of p < 0.05 and  , p < 0.01, compared with LPS treatment alone. E, Human monocytes were treated with different concentrations of IL-4 as indicated for 2 h, and total RNA was isolated for RT-PCR analysis of c-Maf expression (both short and long forms). GAPDH was analyzed as the internal control. F, Human monocytes were treated with IL-4 (1 ng/ml) or LPS (1 μg/ml) or both (IL-4 was added together with LPS) for 8 h, and total RNA was isolated for RT-PCR to examine the long- and short-form c-Maf mRNA expression. GAPDH was analyzed as the internal control. G, Human monocytes were treated with recombinant murine IL-4 (1 ng/ml) or LPS (1 μg/ml) or both (IL-4 was added at +2h) for 8 h, and ChIP assay was conducted as described in Fig. 5B. H, Fetal liver-derived macrophages from c-Maf−/− and c-Maf+/− littermate embryos of gestation day 14.5 were plated into 48-well plates at a density of 0.2 × 106 cells/ml/well. Cells were stimulated with 1 μg/ml LPS, murine IL-4 (1 ng/ml), or LPS + IL-4 (added at +2 h). Supernatants were collected 24 h after LPS treatment for ELISA. Results shown are the summary of four heterozygous and three homozygous knockout embryos. ND, nondetectable.
, p < 0.01, compared with LPS treatment alone. E, Human monocytes were treated with different concentrations of IL-4 as indicated for 2 h, and total RNA was isolated for RT-PCR analysis of c-Maf expression (both short and long forms). GAPDH was analyzed as the internal control. F, Human monocytes were treated with IL-4 (1 ng/ml) or LPS (1 μg/ml) or both (IL-4 was added together with LPS) for 8 h, and total RNA was isolated for RT-PCR to examine the long- and short-form c-Maf mRNA expression. GAPDH was analyzed as the internal control. G, Human monocytes were treated with recombinant murine IL-4 (1 ng/ml) or LPS (1 μg/ml) or both (IL-4 was added at +2h) for 8 h, and ChIP assay was conducted as described in Fig. 5B. H, Fetal liver-derived macrophages from c-Maf−/− and c-Maf+/− littermate embryos of gestation day 14.5 were plated into 48-well plates at a density of 0.2 × 106 cells/ml/well. Cells were stimulated with 1 μg/ml LPS, murine IL-4 (1 ng/ml), or LPS + IL-4 (added at +2 h). Supernatants were collected 24 h after LPS treatment for ELISA. Results shown are the summary of four heterozygous and three homozygous knockout embryos. ND, nondetectable.