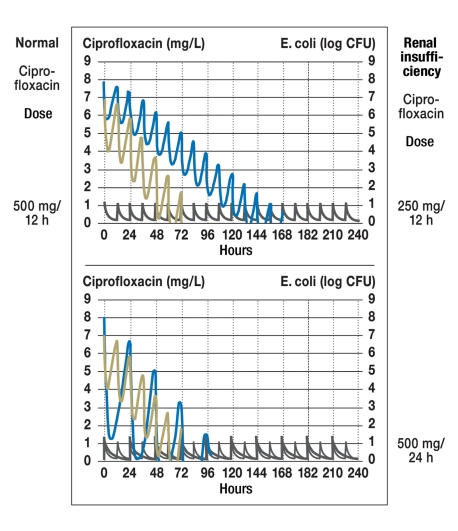
Figure 5.
Dose adjustment for ciprofloxacin, a drug whose effect is concentration-dependent, according to a mechanistic model (23). If renal failure causes a doubling of the half-life from four to eight hours, the dose should not be halved (upper graph); rather, the interval between doses should be doubled (lower graph). If half the normal dose is given, it will take 168 hours for E. coli to be eliminated (above), but if the interval is doubled, the pathogen will be eliminated in 96 hours, as it is when renal function is normal (below);
log CFU = logarithm of colony-forming units