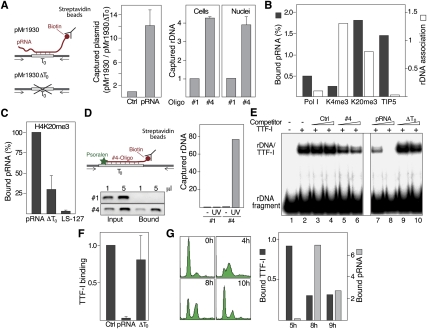
Figure 2.
pRNA interacts with T0 in vivo. (A) Triplex capture assay. (Left) NIH3T3 cells were cotransfected with the rDNA reporter plasmids pMr1930 or pMr1930ΔT0 and biotin-labeled control RNA (Ctrl) or pRNA-205/-1. Cell lysates were incubated with streptavidin-coated beads and captured DNA was analyzed by qPCR. Data are presented as the ratio of captured pMr1930 versus pMr1930ΔT0. (Right) Triplex capture assay using cross-linked chromatin from cells that were transfected with biotinylated oligo #1 or oligo #4 (Cells), or from nuclei that were preincubated with 10 μM biotinylated oligoribonucleotides (Nuclei). (B) pRNA is associated with heterochromatin. ChRIP assay monitoring the level of pRNA associated with chromatin that was precipitated with antibodies against Pol I, H3K4me3 (K4me3), H4K20me3 (K20me3), and TIP5. Data from the initial ChIP are presented as percent of input (light bars), and ChRIP data are presented as pRNA levels normalized to GAPDH mRNA levels (dark bars). (C) pRNA binding to chromatin requires sequences matching T0. Cells were depleted from pRNA by antisense LNA–DNA gapmers; retransfected with synthetic pRNA-205/-1, pRNA-ΔT0, or pRNA-205/-127 (LS-127); and subjected to ChRIP using antibodies against H4K20me3. (D) pRNA interacts directly with T0. Triplex capture assay using native chromatin from cells that were transfected with biotin- and psoralen-labeled oligo #1 or oligo #4. After UV irradiation, DNA associated with the biotinylated oligos was captured with streptavidin-coated beads and analyzed by PCR using 0.2% of input and 1% of bound DNA. The bars on the right represent qPCR data of captured rDNA normalized to β-actin. (E) Binding of TTF-I to its target site is competed by pRNA. EMSA showing binding of TTF-IΔN185 to rDNA in the presence of 100 or 250 pmol (triangles) of a control oligo (#1), an oligoribonucleotide comprising T0 (oligo#4), pRNA-205/-1, or pRNA-ΔT0 (ΔT0). (F) Formation of rDNA:pRNA structures impairs TTF-I binding to rDNA in vivo. ChIP showing the association of TTF-I with the rDNA promoter in the presence of a control RNA (Ctrl), pRNA-205/-1 (pRNA) or pRNA-ΔT0 (ΔT0). (G) Binding of TTF-I and pRNA to rDNA is mutually exclusive. NIH3T3 cells were arrested at G1/S and released into S phase. Cells were harvested in mid (5 h) and late S phase (8 and 9 h after release), and TTF-I binding to rDNA was assayed by ChIP (dark bars). In parallel, chromatin-associated pRNA was determined by ChRIP using antibodies against H4K20me3 (gray bars). FACS analysis demonstrating S-phase progression is shown on the left (n = 2).