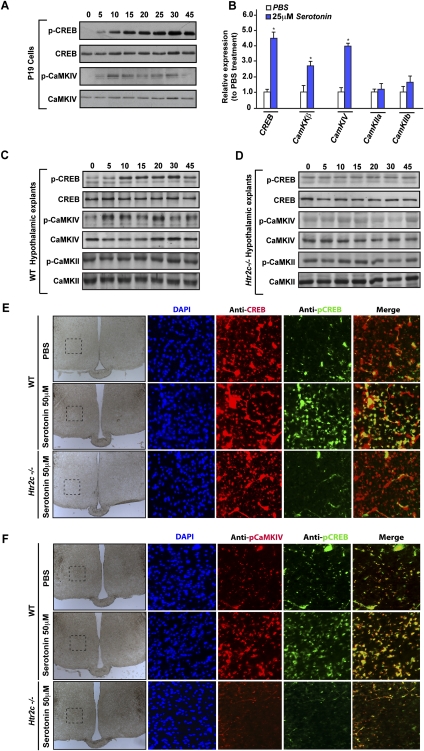
Figure 2.
Serotonin regulates CaMKs and Creb activity and expression. (A) P19 cells differentiated into neurons were treated with 50 μM serotonin for the indicated period of time. Western blot analysis of CREB and CaMKIV phosphorylation performed using p-CREB (s113) and p-CaMKIV (T196) antibodies. (B) Real-time PCR (qPCR) of Creb, CaMKKβ, CaMKIV, CaMKIIa, and CaMKIIb (relative to β-actin expression) in P19 cells after a 4-h treatment with 25 μM serotonin (n = 8 for each measurement). Error bars represent SEM. Student's t-test (*) P < 0.05. (C,D) Western blot analysis of CREB, CaMKIV, and CaMKII phosphorylation in wild-type (C) or in Htr2c−/− (D) hypothalamic explants following treatment with 50 μM serotonin for 5, 10, 15, 20, 30, and 45 min. (E,F) Analysis of the level of CREB phosphorylation by coimmunofluorescence using p-CREB (S133) and CREB antibodies (E) and CREB-CaMKIV phosphorylation using p-CREB (S133) and p-CaMKIV (T196) antibodies (F). Coimmunofluorescence was performed on coronal sections of wild-type (WT) or Htr2c−/− hypothalamic explants treated previously with 50 μM serotonin for 30 min. The first column represents large bright-field images of hypothalamic sections, and the black dashed line delimits the frame for the coimmunofluorescence analysis shown in the following rows. The last column shows the merge between the p-CREB and CREB or p-CREB and p-CaMKIV immunofluorescence images.