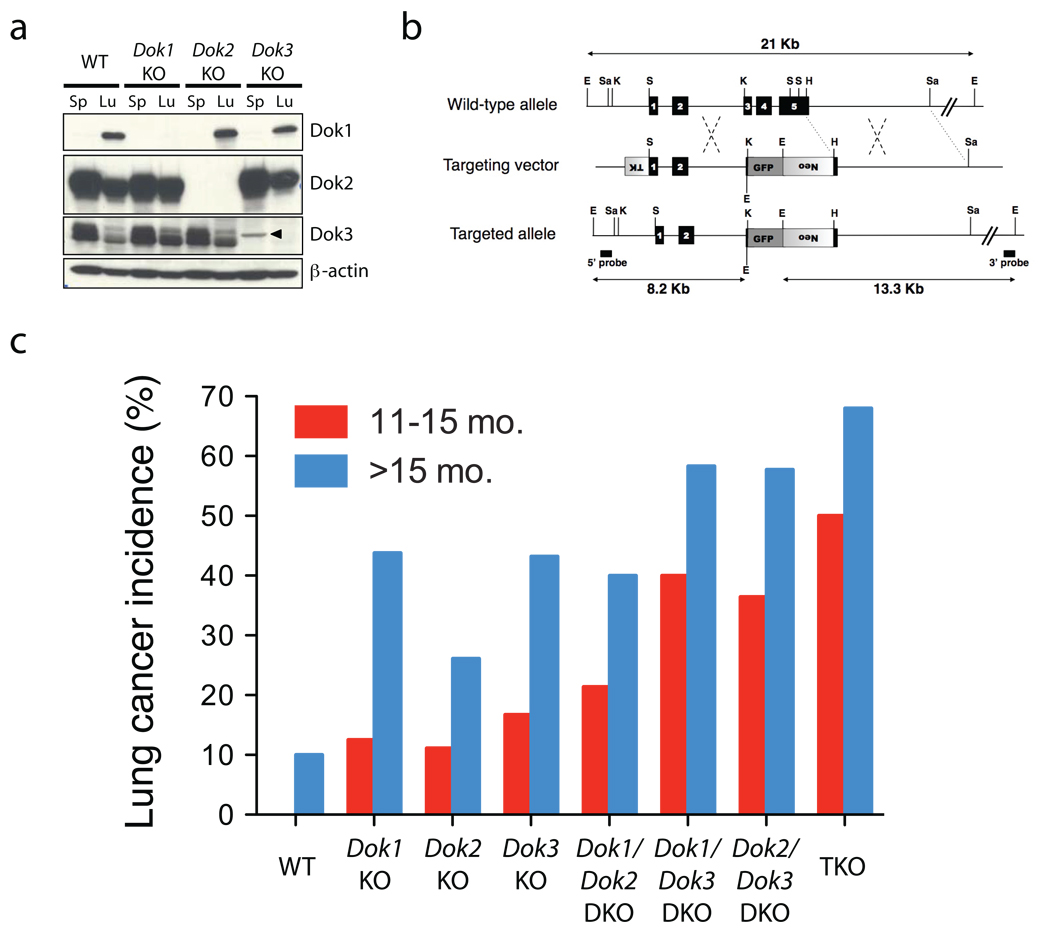
Figure 1. Dok1, Dok2, and Dok3 single and compound KO mice develop lung cancer.
(a) Immunoblot analysis of Dok1, Dok2, Dok3 and β-actin (loading control) proteins in cell lysates of splenocytes (Sp) or homogenized whole lung (Lu) from wild-type (WT), Dok1 KO, Dok2 KO, or Dok3 KO mice. An arrowhead indicates a non-specific band. Dok1 was detected in the spleen lysate at a longer exposure (not shown) and in our previously published work9. (b) Schematic map of the wild-type Dok3 locus (top), the targeting vector (middle) and the predicted targeted locus (bottom). The Dok3 genomic sequence is depicted as a line with solid boxes representing exons 1 to 5. Sequences from the pPNT plasmid are shown as boxes with lines, with shaded boxes representing the neomycin resistance cassette (neo), the HSV thymidine kinase (TK) cassette, or the GFP expression cassette, as indicated. The Dok3 genomic fragments used as probes for Southern-blot analysis are indicated (5’ probe, 3’ probe), as well as the expected fragments (arrows) following hybridization with the probes after digestion with EcoRI. EcoRI (E), SalI (Sa), HindIII (H), KpnI (K), and SmaI (S) sites are shown. (c) Lung adenocarcinoma incidence in Dok1, Dok2, and Dok3 single, double and triple KO mice. Animal numbers and statistics are summarized in Table 1.