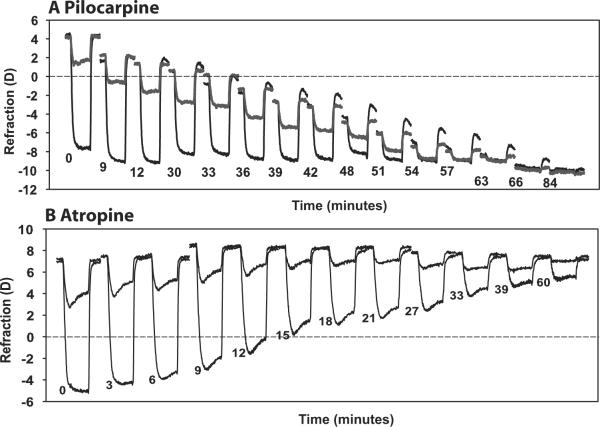
Figure 1.
Representative examples of the time course of the refractive accommodative changes to a sub-maximal and maximal stimulus current amplitude as pilocarpine (A; monkey 38, OD) and atropine (B; monkey 38, OS) takes effect. Each response is an average of three 4-second-long responses, expanded horizontally for visibility. Responses were selected at certain time points: for pilocarpine, resting refraction became approximately 1 D more myopic; for atropine, accommodative amplitude decreased by approximately 1 D. The start time of each response after topical drug application is shown.