Figure 1. Features of the BST-2/tetherin monomer.
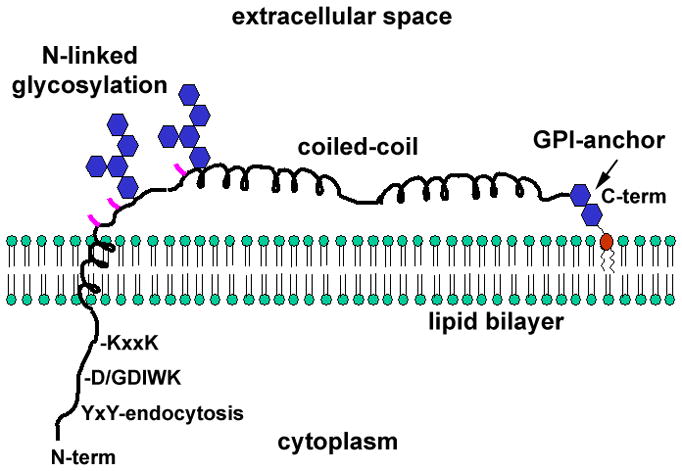
BST-2 binds the lipid bilayer via an N-terminal transmembrane α-helix and a C-terminal glycosylphophastidyl inositol (GPI) anchor. The cytoplasmic domain contains a YxY sequence that directs endocytosis by interacting with the clathrin adaptor AP-2. Non-human primate BST-2 contains an insertion relative to the human protein (D/GDIWK or a similar sequence), which is targeted by lentiviral Nef proteins. The KxxK sequence is ubiquitinated by the K5 protein of KSHV, leading to degradation. The transmembrane region is required for antagonism by HIV-1 Vpu. The ectodomain of the protein contains three cysteines (locations indicated in pink), which drive homo-dimerization. The ectodomain also contains an extended α-helical region that forms a parallel coiled-coil in BST-2 dimers. The transmembrane and GPI membrane anchors, the cysteines, and the integrity of the coiled-coil region are each required for the restriction of virion release.
