Figure 2. Inspiratory CRDPs.
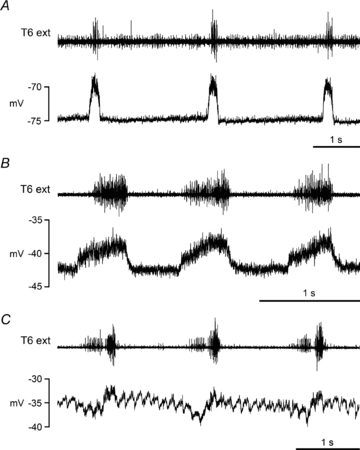
Examples are shown from motoneurones with different identifications and/or animals in different states. A, internal intercostal nerve motoneurone, α-chloralose following halothane; B, unidentified motoneurone, ketamine/xylazine; C; unidentified motoneurone, decerebrate following halothane. The upper trace (T6 external intercostal nerve recording) shows a weak inspiratory discharge in A, a strong inspiratory discharge in B, and inspiratory plus expiratory discharges in C (see de Almeida et al. 2010 for further descriptions). The fast periodic waveform in C (about 8 s−1) is a cardiac movement artefact. The CRDP amplitude was estimated, independently of the artefact, as 4 mV in this instance.
