Figure 3. Biphasic CRDPs.
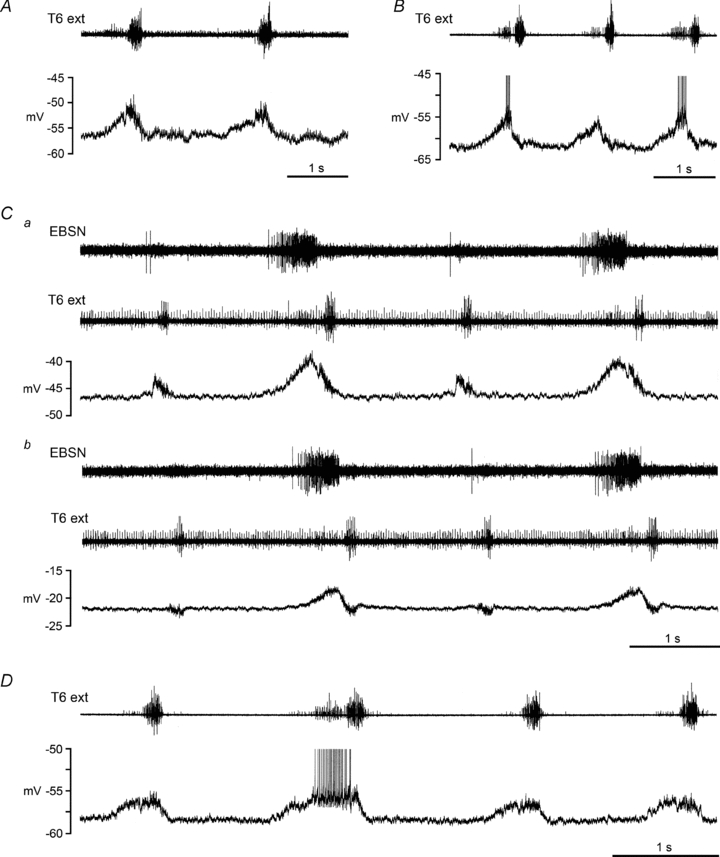
Examples are shown from 4 different internal intercostal nerve motoneurones in 3 different decerebrate rats, following halothane. A, type 1 biphasic CRDP, depolarization largest during inspiration; B–D, type 2 biphasic CRDPs, depolarization largest during expiration. The upper trace (T6 external intercostal nerve recording) shows an inspiratory discharge plus an expiratory discharge for all the examples illustrated, though the expiratory component is weak in A, is only present in alternate cycles in C, and is only strong for one of the cycles in D (see de Almeida et al. 2010 for further descriptions). An EBSN recording is included in C to make clear the expiratory excitation in alternate cycles, since the expiratory discharge in the external intercostal nerve is hard to detect. Both panels of C (a and b) come from the same recording, with b starting 167 s after the end of a, when the cell had depolarized from a membrane potential of −47 mV to −22 mV. Spikes are truncated in B and D.
