Figure 6. Vth is depolarized during fictive weight support and hyperpolarized during ipsilateral scratching.
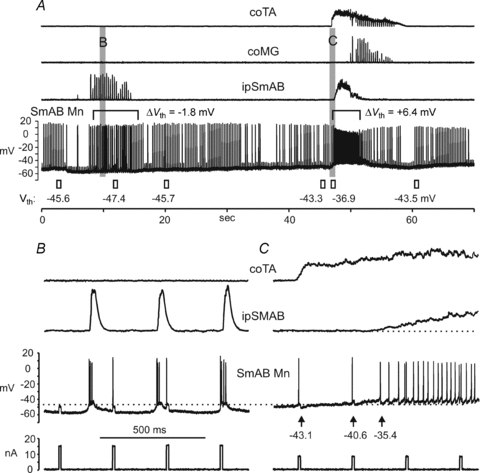
A shows continuous ENG records, first during ipsilateral rhythmic scratching evoked by rubbing the ipsilateral ear (8–15 s in the run), and then during contralateral scratch evoked by rubbing the other ear (48–58 s) in a decerebrate cat without spinal transection. During the approach phase of contralateral scratch (i.e. during tonic activity in the contralateral flexor, coTA) the ipsilateral extensor ipSmAB displays tonic ‘fictive weight support’ activity (48–52 s). The intracellular record from a SmAB motoneurone is shown below the ENGs, and representative values of the Vth measured throughout the run are shown below. Expanded records of the regions indicated by the vertical shaded areas are shown in B and C. Depolarizing current pulses were delivered throughout the run to evoke firing in addition to the spontaneous, scratch-induced firing. The control Vth of −45.6 mV (left-most value) is hyperpolarized by −1.8 mV (to −47.4 mV) during the rhythmic phase of ipsilateral scratch (see B) and recovers a few seconds after the end of ipsilateral scratch activity. During the fictive weight support that begins at about 48 s (see C), Vth depolarized by +6.4 mV from the control value immediately before contralateral scratch began (i.e. from −43.3 to −36.9 mV; see C for values from individual spikes).
