Figure 1. Confocal fluorescence microscopy demonstrates EGFP-identified Cajal–Retzius cells in the CA1 hippocampus of a P24 CXCR4-EGFP mouse.
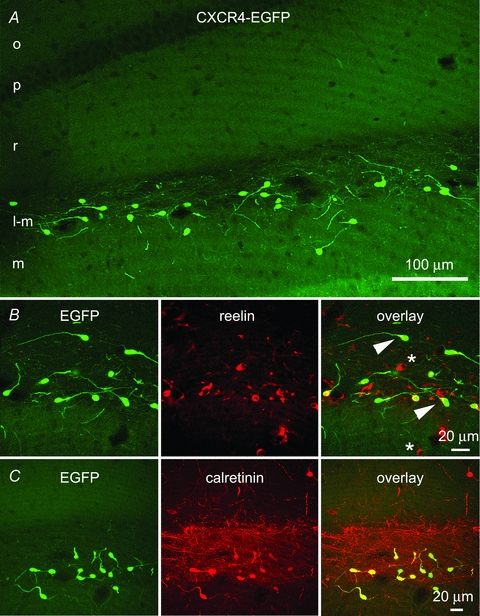
A, EGFP-labelled cells situated along the hippocampal fissure in the stratum lacunosum-moleculare of CA1 and the molecular layer of the fascia dentata have morphological features of previously demonstrated Cajal–Retzius cells. Most of these neurons have a single dendrite that extends opposite to the axon initial segment and that is oriented in different directions. The axons of the EGFP-labelled cells form a dense network in the stratum lacunosum-moleculare. o, stratum oriens; p, stratum pyramidale; r, stratum radiatum; l-m, stratum lacunosum-moleculare; m, stratum moleculare. B, this row of panels shows that all EGFP-labelled cells colocalize reelin, which is enriched at the base of the single dendrite (arrowhead). Reelin-positive/EGFP-negative cells are putative interneurons (*). C, this row of panels indicates that EGFP-positive cells also express calretinin, which highlights the density of the axonal plexus of Cajal–Retzius cells.
