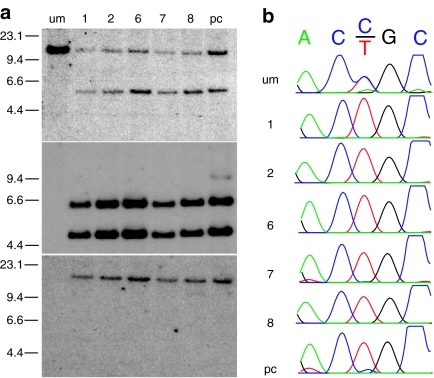
Figure 5.
Southern blot and sequence analysis of KRT14-targeted keratinocytes from a patient with epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS). Ten GFP positive colonies were selected after transduction of patient keratinocytes with the AAVK14e3IFsA gene-targeting vector and sorting for GFP fluorescence. A polyclonal population of sorted GFP positive cells was also analyzed in parallel. Five of the 10 clones grew sufficiently to allow isolation of genomic DNA and analysis by Southern blot. (a) Upper panel: genomic DNA samples from the unmodified patient cells, five GFP positive clones, and the polyclonal KRT14-targeted cells were digested with BamHI and probed with a gene fragment from the KRT14 gene (top) or the GFP gene fragment (middle) as in Figure 4a,b. The same samples were digested with EcoRV and probed with a GFP gene fragment (bottom) as in Figure 4d. The migration positions and size of HindIII digested ΛDNA fragments are shown in kb at the left of each panel. (b) Sequence tracings of the region immediately surrounding the patient's mutation from vector–chromosome junction fragments of each clone and the polyclonal population amplified by PCR using primers located within GFP and 5′ of the location of the EBS-causing mutation in exon 1. Wild type sequence is ACCGC and the EBS-causing mutation is ACTGC producing a R125C substitution of amino acids in the KRT14 protein. pc, polyclonal; um, unmodified.