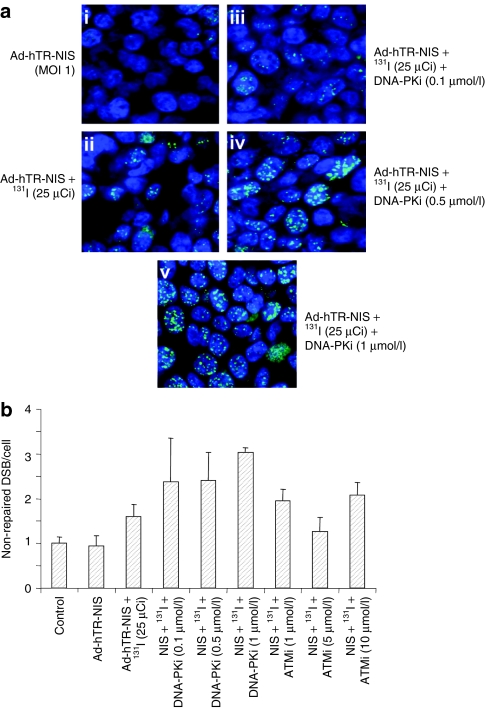
Figure 2.
DNA repair inhibitors maintain NIS-mediated radioisotope-induced DNA double-strand breaks. Effect of DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) inhibitor on maintenance of 131I-mediated phosphorylated γH2AX foci (green dots against blue staining of nuclei) in Ad-hTR-NIS-infected HCT116 cells. (a) Representative confocal microscopic images show (i) very scanty foci in virus-infected cells, (ii) with an increase after treatment with 131I. (iii–v) A dose-dependent increase in γH2AX foci formation was seen in Ad-hTR-NIS-infected cells at 24 hours after application of 25 µCi 131I. (b) Relative number of phospho-γH2AX foci/cell (normalized to the untreated control and displayed as nonrepaired DSBs/cell). Data show a two- to threefold increase in the number of unrepaired DSBs relative to control after treatment with Ad-hTR-NIS, 131I, and DNA repair inhibitors (ATMi and DNA-PKi). Data are representative of at least three repeat experiments. ATMi, ataxia-telangiectasia mutated inhibitor; DSB, double-stranded breaks; NIS, sodium iodide symporter.