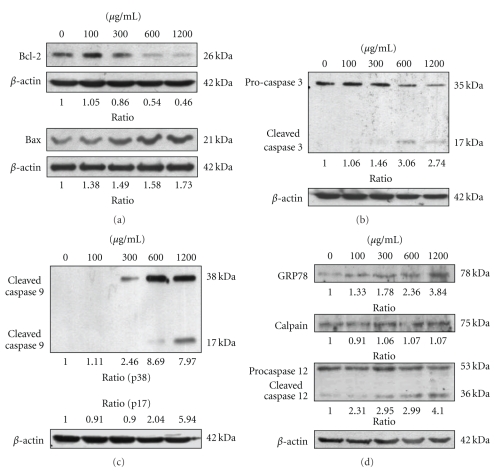
Figure 3.
The mYGJ induces HSC-T6 cell apoptosis through a caspase-dependent pathway. (a) HSC-T6 cells were treated with the indicated dose of mYGJ. The cell lysates were harvested at 72 hours post-treatment and were subjected to Western blot analysis using the anti-Bcl-2 and anti-Bax antibodies, respectively. The band intensity of Bcl-2 or Bax versus β-actin was determined. (b) and (c) HSC-T6 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of mYGJ. The cell lysates were harvested at 72 hours post-treatment and were subjected to Western blot analysis using the anticaspase-3 (b) and anticaspase 9 (c) antibodies, respectively. The band intensity of cleaved caspase 3 or cleaved caspase 9 versus β-actin was determined. (d) HSC-T6 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of mYGJ. The cell lysates were harvested at 72 hours post-treatment and were subjected to Western blot analysis using the anti-GRP78, anti-calpain, and anti-caspase 12 antibodies, respectively. The band intensity of cleaved caspase-3 or cleaved caspase 9 versus β-actin was determined. The expression of β-actin was used for the control of equal protein loading and the relative band intensity ratio to control experiment which did not treat with mYGJ was indicated below the data.