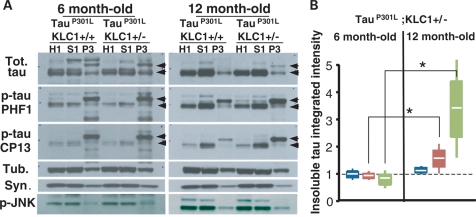
Figure 4.
Transport reduction exacerbates insoluble tau accumulation in the brain stem. (A) Western blots showing total (Tot.) and phosphorylated forms of tau (PHF1, CP13) in homogenate (H1), soluble (S1) and insoluble (P3) fractions after sarkosyl extraction from brain stem of tauP301L;KLC1+/+ and tauP301L;KLC1+/− at 6- and 12-month-old mice. Tubulin (Tub.) and synuclein (Syn.) were used as loading controls. Arrows indicate tau shifts from 51 to 64 kDa. (B) Quantification of three different sarkosyl extractions each corresponding to two pooled mouse brain stems showing tauP301L;KLC1+/− normalized ratios of insoluble to homogenate (P3/H1) for total tau (blue), PHF1 (red) and CP13 (green) at 6- and 12-month-old mice. tauP301L;KLC1+/+ levels were considered as 1. White line, boxes and bars correspond to average, SEM and STDEV, respectively. Mann–Whitney, non-parametric test; n = 6, *P < 0.05).