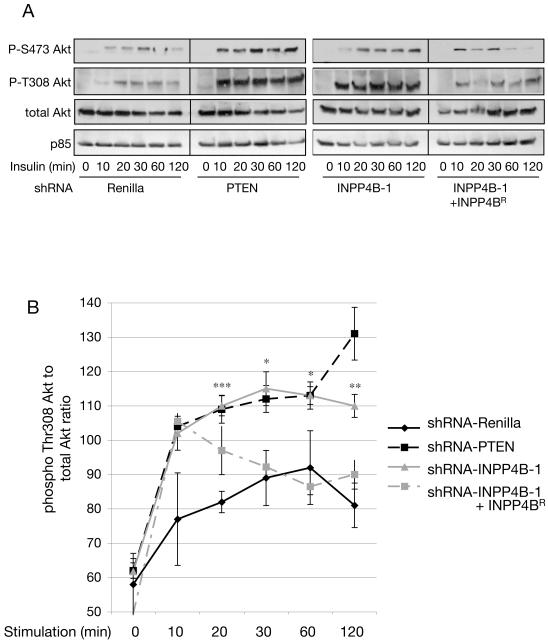
Figure 7. Knocking down the expression of INPP4B increases the duration of AKT activation in response to insulin.
(A) Stable HMEC cell pools expressing shRNA vectors directed against Renilla, PTEN, INPP4B (‘INPP4B-1’) or HMEC cell pools expressing the knockdown resistant INPP4B expression construct in the shRNA-INPP4B-1 cell pool (‘INPP4B-1 + INPP4BR’) were serum-starved and stimulated with 100nM insulin for the indicated time periods. Cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and phospho-Akt detected with specific antibodies in Western blot analysis. INPP4B knockdown cell pools display increased and prolonged phospho-Thr308 and phospho-Ser473 Akt compared to Renilla control knockdown cell pools. Expression of a Flag-tagged INPP4B construct harboring two silent mutations at Ser487 to render it resistant to shRNA knockdown in shRNA-INPP4B-1 cell pools (INPP4BR) reversed prolonged Akt phosphorylation. The results are representative of 4 separate experiments.
(B) Quantification of phospho-Thr308 Akt normalized to total Akt levels (n = 4, *p< 0.1, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). Quantification of each single time point was determined using NIH ImageJ (n = 4). Data are shown as mean +/− SEM.