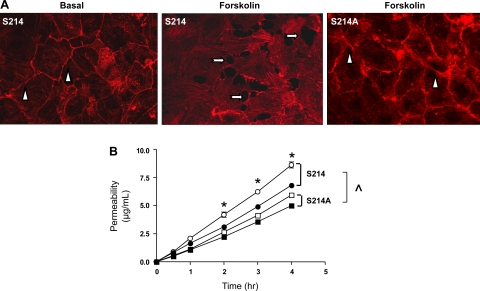
Fig. 5.
S214A mutation blocks the forskolin-induced endothelial cell barrier disruption and -increased permeability. A: phalloidin was used to resolve the cortical actin rim in cells expressing PDE4D41–166 and either S214hTau40 or S214AhTau40. Under basal conditions, a prominent cortical actin rim was denoted (arrowheads). Forskolin (1 μM for 30 min) diminished the cortical actin rim and induced interendothelial cell gaps in S214hTau40-expressing cells (arrows). However, following forskolin stimulation, the cortical actin rim remained intact, and interendothelial cell gaps did not form, in S214AhTau40-expressing cells. B: permeability was measured using fluorescent dextran-Texas Red (mol mass 40,000 Da) Transwell analysis (n = 3). Cells expressing PDE4D41–166 and either S214hTau40 or S214AhTau40 were grown to confluence on Transwell inserts, and permeability was measured over a 5-h time course. Basal permeability measurements (closed symbols) were higher in S214hTau40-expressing cells (S214) than in S214AhTau40-expressing cells (S214A) (^P < 0.05; n = 3). Forskolin (1 μM; open symbols) increased permeability in S214hTau40-expressing cells but was without effect in S214AhTau40-expressing cells (*P < 0.05; n = 3).