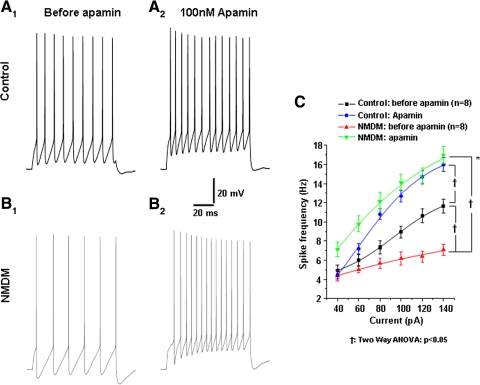
Fig. 10.
Apamin application abolished the difference in spike frequencies of PCMNs in response to current injections between control and NMDM. A, 1 and 2: control; B, 1 and 2: NMDM. Representative traces of AP trains evoked by 1 s-depolarizing current (100 pA) injection during control aCSF and after apamin application in control and NMDM. C. Before apamin, spike frequency was significantly different in control and NMDM (†P < 0.05), which is consistent with Fig. 2C. After apamin application, spike frequency significantly increased in both groups (†P < 0.05), with a significant greater increase in NMDM compared with control (*P < 0.05). There was no difference of spike frequencies between control and NMDM, indicating the difference of spike frequencies between control and NMDM completely diminished.