Fig. 2.
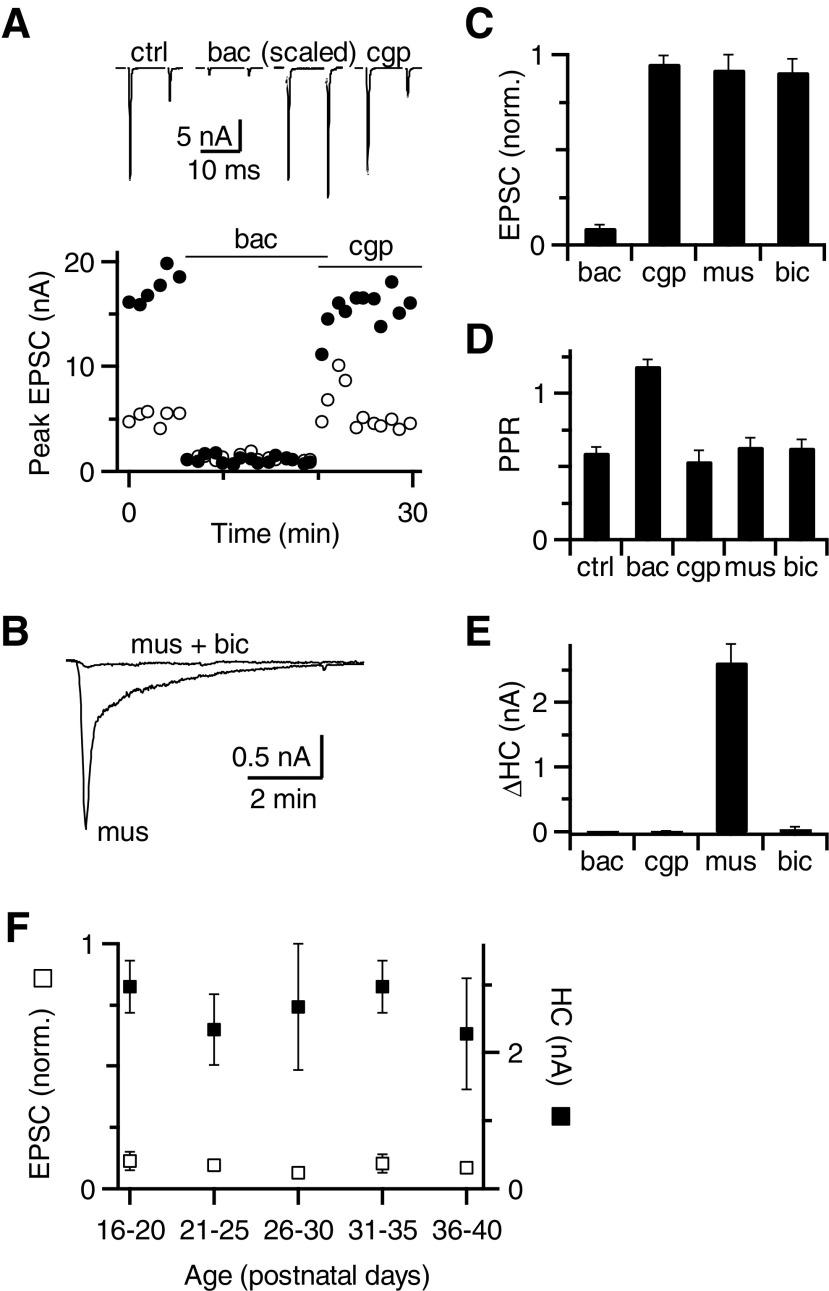
Subtypes of GABARs affecting synaptic transmission. A, top traces: average excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) in response to paired-pulse stimulation before and after application of baclofen and CGP55845. The EPSCs in baclofen are also shown scaled to the control EPSC1 amplitude. Bottom: peak EPSC amplitude measured during the experiment in response to the first (closed circles) and second (open circles) pulses. B: holding current (HC) in response to muscimol application. Bicuculline blocked the effect of muscimol. C–E: effects of GABAR agonists and antagonists on first EPSC amplitude (C), paired-pulse ratio (PPR, D), and HC (E). Only baclofen had a significant effect on EPSC amplitude and PPR (P < 0.001), which were both reversed by CGP55845 (see results). Only muscimol had a significant effect on HC (P < 0.001), which was reversed by bicuculline. Data are averages of 13 (baclofen and CGP) or 16 (muscimol and bicuculline) cells. F: average effect of baclofen on EPSC amplitude (open squares) and muscimol on HC (closed squares) for slices taken from mice of ages P16–P40. Each data point includes 3–6 cells. There were no significant changes in these effects with age.