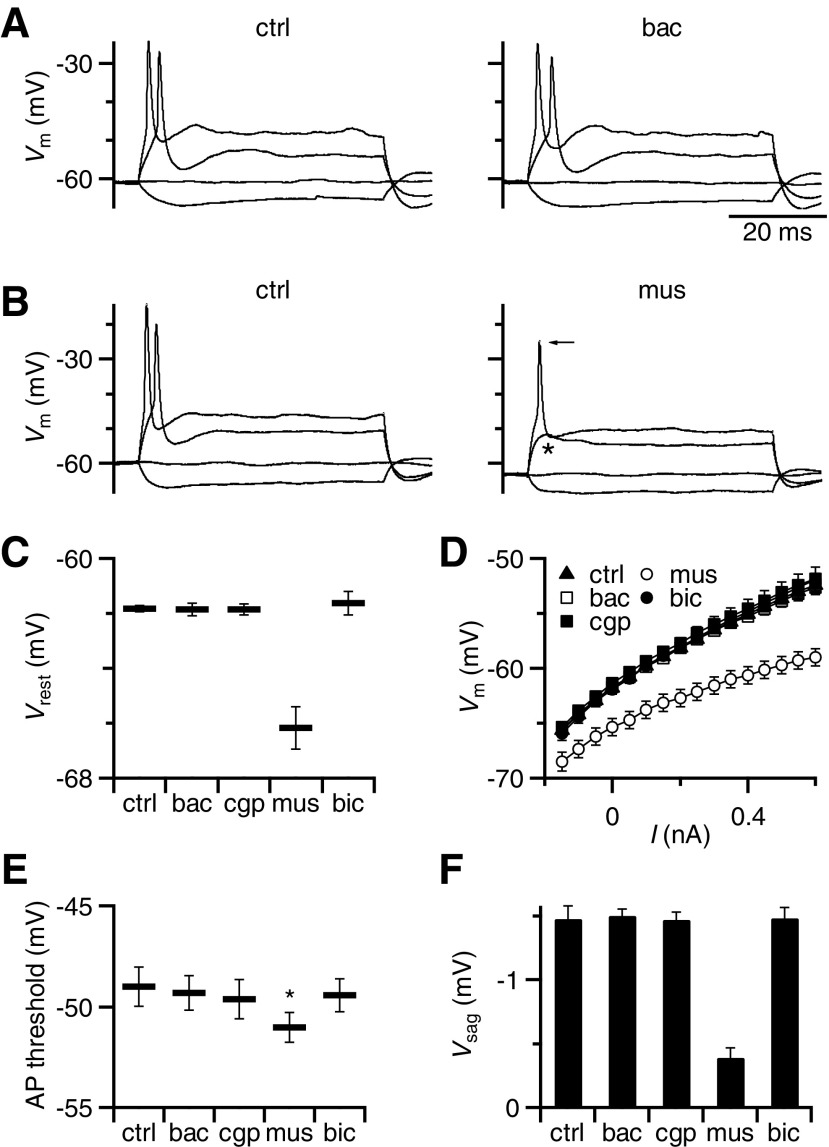
Fig. 3.
Postsynaptic effects of GABAR activation recorded in current-clamp. A: representative effects of baclofen on BC intrinsic properties. Family of responses to current injections ranging from −150 to 600 pA, showing no differences between control conditions (left) and in the presence of baclofen (right). The small depolarization that occurs during hyperpolarizing current pulses (the “sag” potential) reflects Ih activation (see results). B: same experiment as in A, but using muscimol application. Muscimol hyperpolarized the cell, increased the membrane conductance, blocked action potential (AP) firing (asterisk), and decreased the sag potential (Vsag) in response to hyperpolarization. There was also a small decrease in spike amplitude (arrow). C–F: average effects of GABAR agonists and antagonists on BC resting membrane potential (C), input resistance (D), AP threshold (E), and sag potential (F). Muscimol had a significant effect on each of these properties, but baclofen did not. Points are the averages of 8–9 experiments.