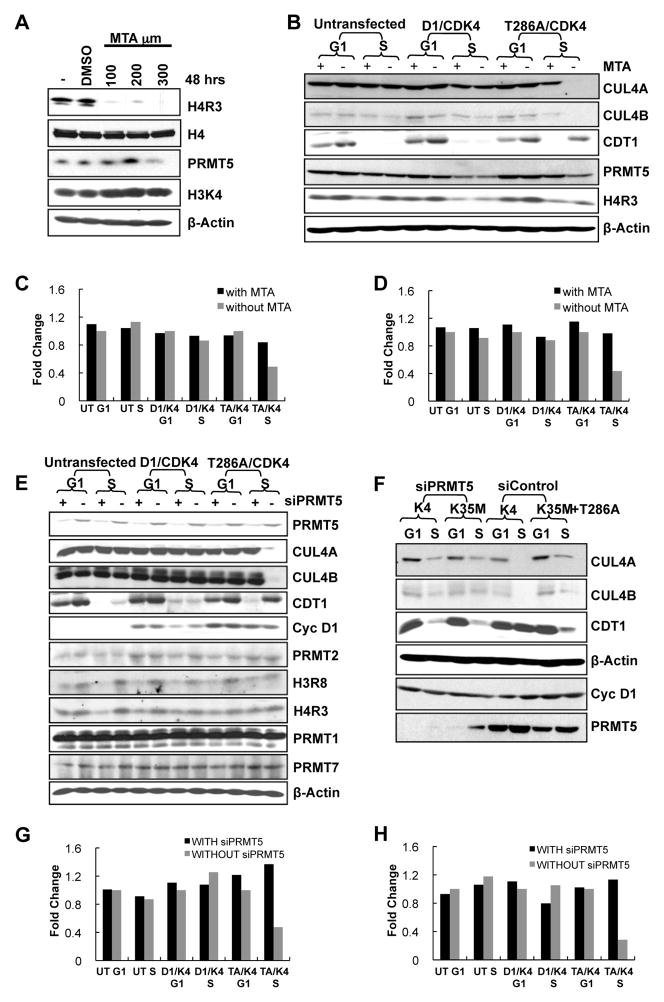
Figure 2. PRMT5/MEP50 mediates cyclin D1T286A/CDK4-dependent CUL4 repression and CDT1 stabilization.
(A) HeLa cells were treated with MTA (5′ Deoxy-5″-methyl-thioadenosine) with concentrations ranging from 100 to 300 μM for 48 hours or vehicle DMSO. The cells were analyzed by western blot as indicated. (B) HeLa cells cultured for 24h in the absence or presence of 100μM MTA were transfected with vectors encoding cyclin D1 or D1T286A and CDK4. 24 hours post-transfection, cells were synchronized with nocodazole for 16–18 hrs; mitotic cells were then separated in two dishes. One was harvested 8h after release (G1-phase). Hydroxyurea was added to the second after release and harvested at 14h to obtain cells in S-phase; lysates were subjected to immunoblot as indicated. (C, D) RNA was collected from HeLa cells treated as in (B). The bars illustrate CUL4A (C) and CUL4B (D) mRNA levels with MTA treatment (first bar) and without MTA treatment (second bar) as analyzed by Real time PCR. One representative experiment of three biological independent experiments is presented. (E) HeLa cells were treated with or without siPRMT5 then transfected with wild type cyclin D1 or D1T286A plasmids along with CDK4. Cells were synchronized as in B, and immunoblotted as indicated. (F) HeLa cells were treated with siPRMT5 or si control smartpool for 24 hours, followed by transfection with cyclin D1T286A along with CDK4 or kinase dead CDK4(K35M) plasmids. Cells were synchronized as in (B), and lysates were immunoblotted as indicated. (G, H) Same as (C-D), except that cells were analyzed with and without siPRMT5 treatment. See also Figure S2.